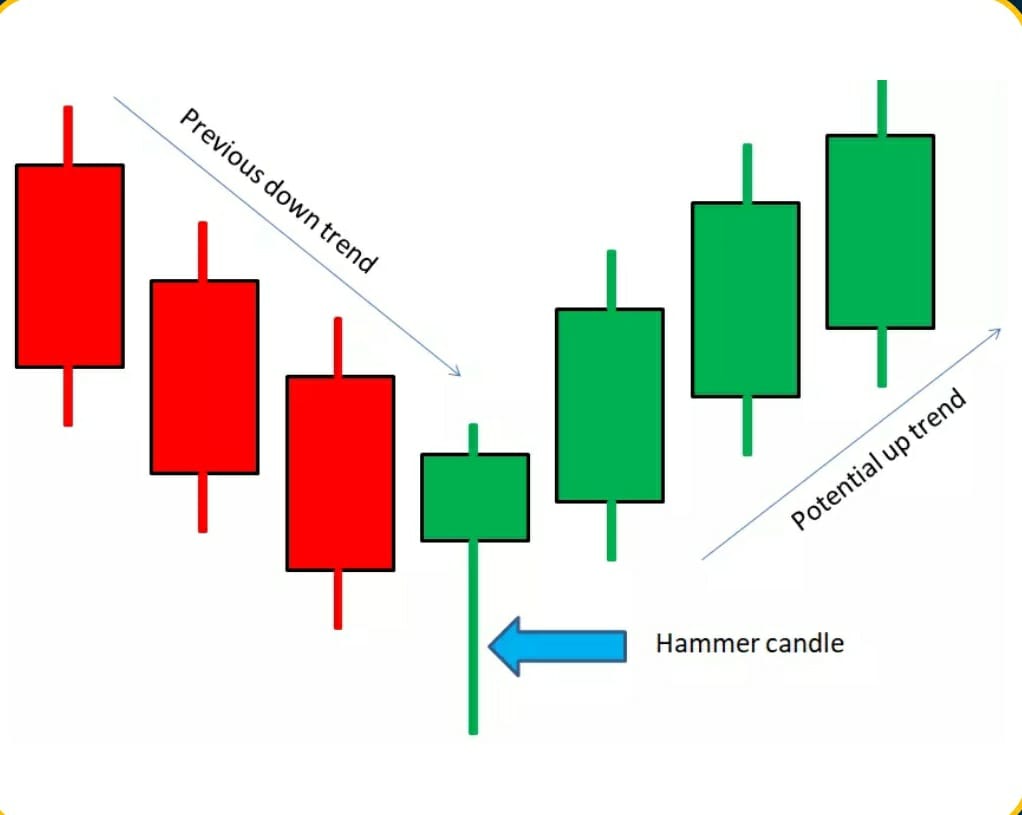
INTRADAY/OPTIONS TRADING
BASIC TO INTERMIDIATE LELVEL
BIGGINER FRINDLY COURSE
CLICK THE BELOW WHATSAPP ICON TO JOIN OUR TRADING WHATSAPP COMMUNITY👇👇👇👇👇
CLICK THE BELOW TELEGRAM ICON TO JOIN OUR LIVE TRADING
TELEGRAM COMMUNITY 👇👇👇👇👇
INTRADY/OPTIONS TRADING BASIC INTERMIDIATE LELVEL
Introduction to the Indian Stock Market:
The Indian stock market is a marketplace where investors can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It functions through two primary stock exchanges: the Bombay Stock Exchange
(BSE) and the National Stock Exchange (NSE).
Platform: BSE and NSE are electronic exchanges where investors place orders to buy or sell shares through brokers.
Participants: Investors, companies, brokers, and SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) are the major stakeholders.
Investment Objectives: Investors aim to profit from capital appreciation (share price increase) or dividends (company payouts). Companies raise capital for growth.
Performance Indicators: Market indices like Sensex (BSE) and Nifty 50 (NSE) reflect overall market movement.
Introduction to the Indian Stock Market:
Indian stock market എന്താണ് എന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണി നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് പബ്ലിക്കായി ട്രേഡ് ചെയ്യപ്പെടുന്ന കമ്പനികളുടെ ഓഹരികൾ വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനുമുള്ള ഒരു വിപണിത്തട്ടാണ്. ഇത് പ്രധാനമായും രണ്ട് സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ വഴിയാണ് പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നത്:
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE): 1875-ൽ സ്ഥാപിതമായ ഏഷ്യയിലെ ഏറ്റവും പഴയ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്.
National Stock Exchange (NSE): 1992-ൽ സ്ഥാപിതമായ ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ആദ്യത്തെ പൂർണ്ണമായും ഓട്ടോമേറ്റഡ് ട്രേഡിംഗ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്.
ഇത് എങ്ങനെ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു?
പങ്കാളികൾ: നിക്ഷേപകർ, കമ്പനികൾ, ബ്രോക്കർമാർ, സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്τια (SEBI) എന്നിവരാണ് പ്രധാന പങ്കാളികൾ.
നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ: മൂലധന വളർച്ചയിൽ നിന്നോ (ഓഹരി വില വർദ്ധന) ഡിവിഡന്റുകളിൽ നിന്നോ (കമ്പനി വിതരണം ചെയ്യുന്ന payout) പ്രയോജനം നേടാനാണ് നിക്ഷേപകർ ലക്ഷ്യമിടുന്നത്. കമ്പനികൾ വളർച്ചയ്ക്കും വിപുലീകരണത്തിനുമായി മൂലധനം സ്വരൂപിക്കുന്നു.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് സമയം: വിപണി പ്രവൃത്തിദിവസങ്ങളിൽ (തിങ്കൾ മുതൽ വെള്ളി വരെ) രാവിലെ 9:15 മുതൽ ഉച്ചയ്ക്ക് 3:30 വരെ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് രീതി: ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് പ്ലാറ്റ്ഫോമിൽ വിലയും അളവും അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി ഓർഡറുകൾ 자동മായി പൊരുത്തപ്പെടുന്നു.
പ്രകടന സൂചകികൾ: വിപണിയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള ചലനം പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുന്ന സെൻസെക്സ് (ബിഎസ്ഇ), നിഫ्टी 50 (എൻഎസ്ഇ) പോലുള്ള സ്റ്റോക്ക് ഇൻഡികസുകൾ.
നിക്ഷേപത്തിന്റെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
മൂലധന വളർച്ചയുടെ സാധ്യത: ദീർഘകാലാടിസ്ഥാനത്തിൽ നിങ്ങളുടെ സമ്പത്ത് വളർത്താനുള്ള അവസരം ഓഹരി വിപണി നൽകുന്നു.
കമ്പനി ഉടമസ്ഥാവകാശം: ഓഹരികൾ വാങ്ങുന്നതിലൂടെ നിങ്ങൾ ഒരു കമ്പനിയിൽ ഭാഗിക ഉടമസ്ഥാവകാശം നേടുകയും അതിന്റെ വിജയത്തിൽ നിന്ന് പ്രയോജനം നേടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
വൈവിധ്യവത്കരണം: നിങ്ങളുടെ പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ വിവിധ മേഖലകളിലായി വൈവിധ്യവത്കരിക്കാൻ ഓഹരി വിപണി നിങ്ങളെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു, ഇത് നിങ്ങളുടെ റിസ്ക് കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു.
പരിഗണിക്കേണ്ട പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
അപകടസാധ്യത: ഓഹരി വിപണി സ്വഭാവത പരമായി അപകടസാധ്യത നിറഞ്ഞതാണ്, പണം നഷ്ടപ്പെടാനുള്ള സാധ്യത എപ്പോഴും നിലനിൽക്കുന്നു.
WHO IS REGULATING INDIAN STOCK MARKET AND HOW?
The Indian stock market is primarily regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Established in 1992, SEBI is a statutory body that functions under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992.
SEBI plays a crucial role in ensuring the fair and orderly functioning of the stock market through various measures:
Formulating Rules and Regulations: SEBI sets the rules for how stock exchanges, listed companies, and intermediaries like brokers operate. This includes listing requirements, insider trading regulations, and investor protection measures.
Registration and Monitoring: SEBI registers stock exchanges, stockbrokers, and other market participants. They also monitor their activities to ensure compliance with regulations.
Investor Protection: SEBI focuses on protecting the interests of investors by promoting transparency and educating them about their rights. They handle complaints and grievances related to the stock market.
Market Development: SEBI works to develop and improve the Indian stock market by introducing new products and services, promoting fair competition among exchanges, and fostering innovation.
In short, SEBI acts as a watchdog, ensuring a level playing field for all participants in the Indian stock market. It fosters a healthy environment that protects investors and facilitates the smooth and transparent growth of the market.
ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക്മാർക്കറ്റിനെ പ്രധാനമായും control ചെയ്യുന്നതരാണ്? എങ്ങനെ ആണ്?
ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിൽ നിയന്ത്രണം വഹിക്കുന്ന വിവിധ
ഘടകങ്ങളും സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളും ഉണ്ട്. അവയിൽ പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടവ
താഴെപ്പറയുന്നവയാണ്:
1. സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (SEBI):
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ നിയന്ത്രണവും മേൽനോട്ടവും
വഹിക്കുന്ന ഏജൻസിയാണ് SEBI. ഓഹരി വിപണിയിലെ
അപകടസാധ്യത കുറയ്ക്കുകയും നിക്ഷേപകരെ
സംരക്ഷിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക എന്നതാണ് SEBI യുടെ പ്രധാന
ലക്ഷ്യം. ഇത് ചെയ്യുന്നതിനായി, SEBI ഇനിപ്പറയുന്ന
കാര്യങ്ങൾ ചെയ്യുന്നു:
നിയമങ്ങൾ നിയമിക്കുകയും നടപ്പിലാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു:
ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്ന എല്ലാവരും പാലിക്കേണ്ട നിയമങ്ങൾ SEBI നിർണ്ണയിക്കുന്നു.
ലിസ്റ്റിംഗ് മാനദണ്ഡങ്ങൾ നിശ്ചയിക്കുന്നു: ഒരു കമ്പനിക്ക് സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചിൽ ലിസ്റ്റ് ചെയ്യാൻ അനുവദിക്കുന്നതിന് മുമ്പ് പാലിക്കേണ്ട മാനദണ്ഡങ്ങൾ SEBI നിശ്ചയിക്കുന്നു.
വ്യാപാര പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ നിരീക്ഷിക്കുന്നു: ഓഹരി വിപണിയിലെ വ്യാപാര പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ SEBI നിരീക്ഷിക്കുകയും അനധികൃത പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ തടയുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
നിക്ഷേപക വിദ്യാഭ്യാസം പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുന്നു: നിക്ഷേപകരെ ഓഹരി വിപണിയെക്കുറിച്ച് ബോധവൽക്കരിക്കാനും അറിവ് നൽകാനും SEBI പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു.
2. സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ: BSE (ബോംബെ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്) and NSE (നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്) എന്നിവയാണ് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ പ്രധാന സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ. ഓഹരി വാങ്ങുന്നതിനും വിൽക്കുന്നതിനുമുള്ള പ്ലാറ്റ്ഫോം നൽകുകയും ട്രേഡിംഗ് നിയമങ്ങൾ നടപ്പാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക എന്നതാണ് സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകളുടെ പ്രധാന പ്രവർത്തനം.
3. ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ: CDSL (സെൻട്രൽ ഡിപോസിറ്ററി സർവീസസ് (ഇന്ത്യ) ലിമിറ്റഡ്) and NSDL (നാഷണൽ സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ഡിപോസിറ്ററി ലിമിറ്റഡ്) എന്നിവയാണ് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ പ്രധാന ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ. ഡീമാറ്റ് രൂപത്തിൽ നിക്ഷേപകരുടെ ഓഹരികൾ സുരക്ഷിതമായി സൂക്ഷിക്കുന്നത് ഡിപോസിറ്ററികളാണ്.
4. ബ്രോക്കർമാർ: നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഓഹരി വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനും സഹായിക്കുന്ന മധ്യസ്ഥരാണ് ബ്രോക്കർമാർ. ഓരോ ട്രേഡിനും ഒരു ബ്രോക്കറേജ് ഫീസ് ബ്രോക്കർമാർ ഈടാക്കുന്നു


INSPITE OF SEBI WHICH ARE THE OTHER PARTICIPANTS REGULATING INDIAN STOCK MARKET
While the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the primary regulator of the Indian stock market, there are other participants who indirectly contribute to its overall stability:
Reserve Bank of India (RBI): Though not a direct regulator, RBI's monetary policies significantly impact the stock market. By controlling interest rates and managing foreign exchange reserves, RBI influences the flow of money into the market, impacting stock prices.
Ministry of Finance (MoF): The MoF sets the overall economic and financial policies of the country. These policies can indirectly impact the stock market by influencing investor sentiment and company performance. The MoF also works with SEBI on formulating regulations for the securities market.
Stock Exchanges (BSE & NSE): While SEBI sets the broad guidelines, the BSE and NSE have their own rulebooks and regulations for trading activities on their platforms. They can suspend trading, penalize members for violations, and implement certain risk management measures within their spheres.
It's important to understand that these entities work in a collaborative manner. SEBI remains the central regulatory body, but the actions of these other participants contribute to a well-functioning and balanced Indian stock market ecosystem.
SEBI യെ കൂടാതെ indian stockmarket നെ control ചെയ്യുന്നതു ആരൊക്കയാണ്
SEBI യെ കൂടാതെ ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിനെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നതിൽ പ്രധാന പങ്കുവഹിക്കുന്ന മറ്റ് സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളും ഘടകങ്ങളും താഴെപ്പറയുന്നവയാണ്:
1. സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ: BSE (ബോംബെ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്) and NSE (നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്) എന്നിവയാണ് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ പ്രധാന സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ. ഓഹരി വാങ്ങുന്നതിനും വിൽക്കുന്നതിനുമുള്ള പ്ലാറ്റ്ഫോം നൽകുകയും ട്രേഡിംഗ് നിയമങ്ങൾ നടപ്പാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക എന്നതാണ് ഇവയുടെ പ്രധാന പ്രവർത്തനം.
2. ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ: CDSL (സെൻട്രൽ ഡിപോസിറ്ററി സർവീസസ് (ഇന്ത്യ) ലിമിറ്റഡ്) and NSDL (നാഷണൽ സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ഡിപോസിറ്ററി ലിമിറ്റഡ്) എന്നിവയാണ് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ പ്രധാന ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ. ഡീമാറ്റ് രൂപത്തിൽ നിക്ഷേപകരുടെ ഓഹരികൾ സുരക്ഷിതമായി സൂക്ഷിക്കുന്നത് ഇവയാണ്.
3. ബ്രോക്കർമാർ: നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഓഹരി വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനും സഹായിക്കുന്ന മധ്യസ്ഥരാണ് ബ്രോക്കർമാർ. ഓരോ ട്രേഡിനും ഒരു ബ്രോക്കറേജ് ഫീസ് ഇവർ ഈടാക്കുന്നു.
4. നിക്ഷേപകർ: ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ പണം നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്ന വ്യക്തികളും സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളുമാണ് നിക്ഷേപകർ. ഓഹരി വാങ്ങുന്നതിലൂടെ, കമ്പനികളുടെ ഭാഗിക ഉടമസ്ഥാവകാശം നേടുകയും അവയുടെ വിജയത്തിൽ നിന്ന് പ്രയോജനം നേടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
5. ക്ലിയറിംഗ് ഹൗസുകളും സെറ്റിൽമെന്റ് സംവിധാനങ്ങളും: ഓഹരി ട്രേഡുകൾക്ക് സുഗമമായ സെറ്റിൽമെന്റ് ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നത് ഇവയാണ്.
6. ക്രെഡിറ്റ് റേറ്റിംഗ് ഏജൻസികൾ: കമ്പനികളുടെയും അവയുടെ ഡെബ്റ്റ് സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളുടെയും സാമ്പത്തിക ശക്തി വിലയിരുത്തുന്നത് ഇവയാണ്.
SEBI യെ കൂടാതെ indian market നെ control ചെയ്യുന്നതു ആരൊക്കയാണ്കുന്നതിലൂടെ നിക്ഷേപകരെ സഹായിക്കുന്നതിൽ മാധ്യമങ്ങൾ പ്രധാന പങ്ക് വഹിക്കുന്നു.
ഓരോ ഘടകവും ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ കാര്യക്ഷമമായ പ്രവർത്തനത്തിന് സംഭാവന ചെയ്യുകയും നിക്ഷേപകരെ സംരക്ഷിക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
ഓഹരി വിപണിയെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നതിൽ SEBI ക്ക് നിർണായക പങ്കുണ്ടെങ്കിലും, മുകളിൽ പറഞ്ഞ മറ്റ് സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളും ഘടകങ്ങളും ഒരു സുഗമവും സുതാര്യവുമായ വിപണി ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നതിൽ പ്രധാന പങ്കുവഹിക്കുന്നു.
DEFINE NSE AND BSE
NSE and BSE are the two main stock exchanges in India, functioning as marketplaces where investors can buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. Here's a breakdown of each:
Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE):
Established: 1875 (Asia's oldest stock exchange)
Location: Mumbai
Trading Platform: Electronic (since 1995)
Index: Sensex (tracks the performance of the 30 largest and most actively traded companies on the BSE)
Known for: Its historical significance and evolving practices. It can be a good choice for beginners or investors seeking steady, lower-risk investments.
National Stock Exchange (NSE):
Established: 1992 (First fully automated trading exchange in India)
Location: Mumbai
Trading Platform: Fully electronic
Index: Nifty 50 (represents the 50 largest companies by market capitalization on the NSE)
Known for: Technological innovation, transparency, and
high trading volume. It may be preferred by investors seeking a more active trading environment




DEFINE CDSL AND NSDL
CDSL and NSDL are not directly involved in regulating the Indian stock market, but they play a critical role in its infrastructure. They are both depositories, which means they handle the electronic storage and movement of securities like stocks and bonds.
Here's a breakdown of their function:
Dematerialization: In the past, stock certificates were physical documents. CDSL and NSDL facilitate the dematerialization process, converting these certificates into electronic form. This makes trading faster, safer, and more efficient.
Holding Securities: These depositories hold your shares electronically in your Demat account, which you access through a broker.
Settlement: When you buy or sell shares, CDSL or NSDL ensures the smooth transfer of securities between your account and the seller's account.
Key Similarities:
Both CDSL (Central Depository Services (India) Limited) and NSDL (National Securities Depository Limited) are government-registered depositories.
They offer similar services for electronic storage and movement of securities.
Both require investors to have a Demat account to hold shares electronically.
Key Differences:
Market Share: NSDL is the older and larger depository, holding a majority of the market share. CDSL is a strong competitor with a growing market presence.
Year of Establishment: NSDL was established in 1996, while CDSL came into existence in 1999.
In essence, both CDSL and NSDL act as the backbone for the electronic securities market in India, ensuring secure and efficient transactions.
CDSL and NSDL എന്താണ് എന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ നേരിട്ടുള്ള നിയന്ത്രണത്തിൽ നിന്ന് വ്യത്യസ്തമായി, നിക്ഷേപ സുരക്ഷയുടെ കാര്യത്തിൽ അടിസ്ഥാന സൗകര്യങ്ങൾ ഒരുക്കുന്ന രണ്ട് പ്രധാന സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളാണ് സിഡിഎസ്എൻഎസ്ഡിഎൽ.
ഇവ രണ്ടും ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ ആണ്, അതായത് ഓഹരികളും ബോണ്ടുകളും പോലുള്ള സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളുടെ ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് സ്റ്റോറേജും ചലനങ്ങളും കൈകാര്യം ചെയ്യുന്ന സ്ഥാപനങ്ങൾ.
ഇവയുടെ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ ഇങ്ങനെ:
ഡീമാറ്റീരിയലൈസേഷൻ: പണ്ടുകാലത്ത്, ഓഹരി സർട്ടിഫിക്കറ്റുകൾ ഫിസിക്കൽ രേഖകളായിരുന്നു. സിഡിഎസ്എൻഎസ്ഡിഎൽ എന്നിവ ഈ സർട്ടിഫിക്കറ്റുകളെ ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് രൂപത്തിലേക്ക് പരിവർത്തനം ചെയ്യുന്ന ഡീമാറ്റീരിയലൈസേഷൻ പ്രക്രിയ സുഗമമാക്കുന്നു. ഇത് വ്യാപാരം വേഗത്തിലും സുരക്ഷിതമായും കൂടുതൽ കാര്യക്ഷമമാക്കുന്നു.
സെക്യൂരിറ്റികൾ സൂക്ഷിക്കൽ: ഈ ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ നിങ്ങളുടെ ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിൽ ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് രൂപത്തിൽ നിങ്ങളുടെ ഓഹരികൾ സൂക്ഷിക്കുന്നു, ബ്രോക്കർ വഴി നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ഇത് ആക്സസ് ചെയ്യാൻ കഴിയും.
സെറ്റിൽമെന്റ്: നിങ്ങൾ ഓഹരികൾ വാങ്ങുകയോ വിൽക്കുകയോ ചെയ്യുമ്പോൾ, നിങ്ങളുടെ അക്കൗണ്ടും വിൽപ്പനക്കാരന്റെ അക്കൗണ്ടും തമ്മിലുള്ള സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളുടെ തടസ്സമില്ലാത്ത കൈമാറ്റം
സിഡിഎസ്എൻഎസ്ഡിഎൽ ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നു.
സിഡിഎസ്എൻഎസ്ഡിഎൽ എന്നിവ തമ്മിലുള്ള പ്രധാന സാമ്യതകൾ:
സെൻട്രൽ ഡिपॉസിറ്ററി സർവീസസ് (ഇന്ത്യ) ലിമിറ്റഡ് (CDSL) ಮತ್ತು നാഷണൽ സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ഡिपॉസിറ്ററി ലിമിറ്റഡ് (NSDL) എന്നിവ സർക്കാർ രജിസ്റ്റർ ചെയ്ത ഡിപോസിറ്ററികളാണ്.
ഇവ സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളുടെ ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് സ്റ്റോറേജും ചലനങ്ങളും സമാനമായ സേവനങ്ങൾ നൽകുന്നു.
ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് രീതിയിൽ ഓഹരികൾ സൂക്ഷിക്കുന്നതിന് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഒരു ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട് ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കണം.
പ്രധാന വ്യത്യാസങ്ങൾ:
വിപണി വിഹിതം: NSDL പഴയതും വലിയതുമായ ഡിപോസിറ്ററിയാണ്, വിപണി വിഹിതത്തിൽ ഭൂരിഭാഗവും വഹിക്കുന്നു. സിഡിഎസ്എൻഎസ്ഡിഎൽ വളർന്നുവരുന്ന വിപണി സാന്നിധ്യമുള്ള ശക്തനായ മത്സരാർത്ഥിയാണ്.
സ്ഥാപന വർഷം: NSDL 1996 ൽ സ്ഥാപിതമായി, ενώ CDSL 1999 ൽ നിലവിൽ വന്നു.
IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET WHO IS PROVIDING SECURITY TO OUR INVESTMENT OR TRADING FUND IN DEMAT ACCOUNT
The security of your investments in a Demat account in the Indian stock market is a multi-layered process involving several entities:
Depositories (CDSL & NSDL): These act as the custodians of your securities in electronic form. They hold your shares securely and ensure their safekeeping.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): SEBI regulates the functioning of depositories and ensures they maintain strict safety standards for investor holdings.
Brokers: Reputable brokers have strong internal controls and cybersecurity measures to protect client data and prevent unauthorized access to Demat accounts.
Demat Account Features: Demat accounts themselves come with security features like two-factor authentication and login limitations to minimize unauthorized access.
KYC (Know Your Customer) Compliance: Brokers are required by SEBI to perform KYC verification on all clients. This helps prevent identity theft and fraudulent account openings.
It's important to remember:
While the system is robust, it's advisable to choose a reputed broker with a strong track record of security.
Maintain strong passwords for your Demat account and avoid sharing them with anyone.
Be cautious of unsolicited calls or emails claiming to be from your broker or depository. SEBI and legitimate institutions won't ask for your login credentials via such channels.
Regularly monitor your Demat account statements to identify any suspicious activity.
By understanding these layers of security and practicing caution, you can minimize the risk associated with Demat accounts.
IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET WHO IS PROVIDING SECURITY TO OUR INVESTMENT OR TRADING FUND IN DEMAT ACCOUNT
The security of your investments in a Demat account in the Indian stock market is a multi-layered process involving several entities:
Depositories (CDSL & NSDL): These act as the custodians of your securities in electronic form. They hold your shares securely and ensure their safekeeping.
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI): SEBI regulates the functioning of depositories and ensures they maintain strict safety standards for investor holdings.
Brokers: Reputable brokers have strong internal controls and cybersecurity measures to protect client data and prevent unauthorized access to Demat accounts.
Demat Account Features: Demat accounts themselves come with security features like two-factor authentication and login limitations to minimize unauthorized access.
KYC (Know Your Customer) Compliance: Brokers are required by SEBI to perform KYC verification on all clients. This helps prevent identity theft and fraudulent account openings.
It's important to remember:
While the system is robust, it's advisable to choose a reputed broker with a strong track record of security.
Maintain strong passwords for your Demat account and avoid sharing them with anyone.
Be cautious of unsolicited calls or emails claiming to be from your broker or depository. SEBI and legitimate institutions won't ask for your login credentials via such channels.
Regularly monitor your Demat account statements to identify any suspicious activity.
By understanding these layers of security and practicing caution, you can minimize the risk associated with Demat accounts.
Indian stock market ൽ demat അക്കൗണ്ട് ൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്ന നമ്മുടെ investment amount നും trading capital നും ആരാണ് security തരുന്നത്
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ നിങ്ങളുടെ ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിലെ നിക്ഷേപ തുകയ്ക്കും വ്യാപാര മൂലധനത്തിനും സുരക്ഷ നൽകുന്നത് ഒന്നിലധികം ഘടകങ്ങൾ ചേർന്ന ഒരു സംവിധാനമാണ്:
1. ഡിപോസിറ്ററികൾ (സിഡിഎസ്എൽ & NSDL): ഡിമാറ്റ് രൂപത്തിൽ നിങ്ങളുടെ സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളുടെ സംരക്ഷകരായി ഇവ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു. അവ നിങ്ങളുടെ ഓഹരികൾ സുരക്ഷിതമായി സൂക്ഷിക്കുകയും അവയുടെ സുരക്ഷ ഉറപ്പാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
2. സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (SEBI): ഡിപോസിറ്ററികളുടെ പ്രവർത്തനം SEBI നിയന്ത്രിക്കുകയും നിക്ഷേപകരുടെ ഹോൾഡിംഗുകൾക്ക് കർശനമായ സുരക്ഷാ മാനദണ്ഡങ്ങൾ പാലിക്കുന്നുവെന്ന് ഉറപ്പാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
3. ബ്രോക്കർമാർ: പ്രശസ്തരായ ബ്രോക്കർമാർക്ക് ക്ലയൻറ് ഡാറ്റ സംരക്ഷിക്കാനും ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടുകളിലേക്കുള്ള അനധികൃത പ്രവേശനം തടയാനും ശക്തമായ ആന്തരിക നിയന്ത്രണങ്ങളും സൈബർ സുരക്ഷാ നടപടികളും ഉണ്ട്.
4. ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട് സവിശേഷതകൾ: അനധികൃത പ്രവേശനം കുറയ്ക്കുന്നതിന് ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടുകൾ രണ്ട് ഘട്ട ധ്രുവീകരണം, ലോഗിൻ പരിമിതികൾ തുടങ്ങിയ സുരക്ഷാ സവിശേഷതകളോടെയാണ് വരുന്നത്.
5. KYC (നോർ യുവർ കസ്റ്റമർ) അനുസരണം: എല്ലാ ക്ലയന്റുകളിലും KYC പരിശോധന നടത്താൻ SEBI ബ്രോക്കർമാരോട് ആവശ്യപ്പെടുന്നു. ഇത് totožnost krádežിനെയും തട്ടിപ്പ് അക്കൗണ്ടുകൾ തുറക്കുന്നതിനെയും തടയാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
ഓർത്തിരിക്കേണ്ട കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
സംവിധാനം യഥാർത്ഥത്തിൽ ശക്തമാണെങ്കിലും, ശക്തമായ സുരക്ഷാ റെക്കോർഡുള്ള ഒരു പ്രശസ്ത ബ്രോക്കറെ തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുന്നത് ഉചിതമാണ്.
നിങ്ങളുടെ ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിനായി ശക്തമായ പാസ്വേഡുകൾ സൂക്ഷിക്കുകയും അവ ആരോടെങ്കിലും പങ്കിടാതിരിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക.
നിങ്ങളുടെ ബ്രോക്കറിൽ നിന്നോ ഡിപോസിറ്ററിയിൽ നിന്നോ ഉള്ളതായി അവകാശപ്പെടുന്ന അന്വേഷണങ്ങൾക്കോ ഇമെയിലുകൾക്കോ ശ്രദ്ധിക്കുക. SEBI-യും നിയമാനുസൃത സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളും ഇത്തരം ചാനലുകളിലൂടെ നിങ്ങളുടെ ലോഗിൻ ക്രെഡൻഷ്യലുകൾ ചോദിക്കില്ല.
സംശയാസ്പദമായ പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ കണ്ടെത്തുന്നതിന് നിങ്ങളുടെ ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട് സ്റ്റേറ്റ്മെന്റുകൾ പതിവായി നിരീക്ഷിക്കുക.
DEFINE FINACIAL INDUSTRY REGULATORY AUTHORITY
(FINRA)
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) is a self-regulatory organization (SRO) in the United States that oversees and regulates broker-dealer firms and exchange markets. Here's a breakdown of its key functions:
Protecting Investors: FINRA's primary mission is to safeguard investors by ensuring fair and honest practices in the securities industry. They achieve this by:
Writing and enforcing rules that govern the conduct of member firms and their representatives.
Conducting examinations and investigations to identify and address potential misconduct.
Maintaining a database of disciplinary actions against brokers and firms.
Market Oversight: FINRA also plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the securities markets:
They set standards for fair and orderly trading practices.
They monitor trading activity for potential manipulation or illegal activity.
They oversee the listing and delisting of securities on exchanges.
Education and Licensing: FINRA establishes qualification standards and administers licensing exams for individuals who want to work as securities brokers or representatives. They also offer educational resources for investors to learn about the financial markets.
Key Points to Remember:
FINRA is not a government agency, but it operates under the oversight of the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
FINRA membership is mandatory for most broker-dealer firms that operate in the United States.
Investors can file complaints with FINRA if they believe they have been mistreated by a broker or brokerage firm.
Financial industry REGULATORY authority എന്താണെന്നു വിശദമാക്കുക (U.S)
സാമ്പത്തിക വ്യവസ്ഥയിൽ സുസ്ഥിരതയും സുതാര്യതയും ഉറപ്പാക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്ന ഒരു സ്ഥാപനമാണ് സാമ്പത്തിക വ്യവസായ നിയന്ത്രണ അധികാരം (FIRA). ഓഹരി വിപണി, ബാങ്കിംഗ്, ഇൻഷുറൻസ് തുടങ്ങിയ മേഖലകളിൽ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്ന സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളെയും വ്യക്തികളെയും നിയന്ത്രിക്കുകയും മേൽനോട്ടം വഹിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക എന്നതാണ് FIRA-യുടെ പ്രധാന ലക്ഷ്യം.
FIRA-യുടെ പ്രധാന പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ:
നിയമങ്ങൾ നിയമിക്കുകയും നടപ്പിലാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുക: സാമ്പത്തിക വ്യവസ്ഥയിൽ സുരക്ഷയും സുസ്ഥിരതയും ഉറപ്പാക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്ന നിയമങ്ങൾ FIRA വികസിപ്പിക്കുകയും നടപ്പിലാക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
നിക്ഷേപകരെ സംരക്ഷിക്കുക: തട്ടിപ്പ്, മാർക്കറ്റ് കൃത്രിമത്വം, അനധികൃത പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ തുടങ്ങിയവയിൽ നിന്ന് നിക്ഷേപകരെ സംരക്ഷിക്കാൻ FIRA പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു.
വിപണി മേൽനോട്ടം: സാമ്പത്തിക വിപണികളുടെ പ്രവർത്തനം നിരീക്ഷിക്കുകയും അനധികൃത പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ കണ്ടെത്തുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു FIRA.
വിദ്യാഭ്യാസവും അവബോധവും: സാമ്പത്തിക വിപണിയെക്കുറിച്ച് നിക്ഷേപകരെയും പൊതുജനങ്ങളെയും ബോധവൽക്കരിക്കാൻ FIRA പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു.
FIRA-യുടെ പ്രാധാന്യം:
സുസ്ഥിരമായ സാമ്പത്തിക വ്യവസ്ഥ: സാമ്പത്തിക വ്യവസ്ഥയിൽ സുസ്ഥിരതയും സുതാര്യതയും ഉറപ്പാക്കാൻ FIRA സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
നിക്ഷേപക സംരക്ഷണം: തട്ടിപ്പിൽ നിന്നും മറ്റ് അനധികൃത പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങളിൽ നിന്നും നിക്ഷേപകരെ സംരക്ഷിക്കാൻ FIRA സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
വിപണി കാര്യക്ഷമത: സാമ്പത്തിക വിപണികൾ കാര്യക്ഷമമായും സുതാര്യമായും പ്രവർത്തിക്കാൻ FIRA സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
ഇന്ത്യയിലെ FIRA:
ഇന്ത്യയിൽ, സാമ്പത്തിക വ്യവസായത്തെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്ന ഒരൊറ്റ FIRA ഇല്ല. പകരം, ഓരോ സാമ്പത്തിക മേഖലയെയും നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്ന പ്രത്യേക റെഗുലേറ്റർമാർ ഉണ്ട്.
സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (SEBI): ഓഹരി വിപണിയെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നത് SEBI ആണ്.
റിസർവ് ബാങ്ക് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (RBI): ബാങ്കിംഗ് സംവിധാനത്തെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നത് RBI ആണ്.
ഇൻഷുറൻസ് റെഗുലേറ്ററി ആൻഡ് ഡെവലപ്മെന്റ് അതോറിറ്റി (IRDAI): ഇൻഷുറൻസ് മേഖലയെ നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നത് IRDAI ആണ്.
WHICH ARE THE MAIN FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS IN INDIA
The main financial instruments in India can be broadly categorized into two groups: equity and debt instruments.
Equity Instruments
Stocks (Shares): These represent ownership in a company. When you buy a company's stock, you become a shareholder and are entitled to a portion of the company's profits (dividends) and voting rights on certain company decisions.
📷
Mutual Funds: These are pooled investment vehicles that allow you to invest alongside other individuals in a professionally managed basket of assets, which could include stocks, bonds, or other securities. Mutual funds offer diversification and professional management, which can help to reduce risk and improve returns.
📷
Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs): Similar to mutual funds, ETFs are baskets of securities that trade on stock exchanges like stocks. However, unlike mutual funds, ETFs are bought and sold throughout the trading day at market prices.
📷
Debt Instruments
Bonds: These are essentially loans that you make to a company or government. When you buy a bond, you are essentially lending money to the issuer for a specific period at a fixed interest rate. Bonds are generally considered to be less risky than stocks, but they also offer lower potential returns.
Debentures: These are similar to bonds, but they are unsecured debt instruments. This means that if the issuer defaults on the loan, you may not get your money back. Debentures typically offer higher interest rates than bonds to compensate for the additional risk.
Fixed Deposits (FDs): These are time deposits offered by banks and other financial institutions. When you invest in an FD, you agree to deposit a certain amount of money for a fixed period of time. In return, the bank will pay you a fixed interest rate on your deposit. FDs are a relatively safe investment option, but they also offer lower potential returns than stocks or bonds.
These are just some of the main financial instruments available in India. The best investment option for you will depend on your individual risk tolerance, investment goals, and time horizon. It is important to do your research and consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions.
DEMAT ACCOUNT AND TRADING ACCOUNT
Trading Account and Demat Account: Keys to Stock Market Investing
The stock market allows you to invest in companies by buying and selling shares. To participate, you'll need two essential accounts: a trading account and a demat account. Here's a breakdown of each:
Trading Account:
Function: This account acts as your gateway to buying and selling shares in the stock market.
Process: You open a trading account with a broker, a licensed intermediary who facilitates your trades on the stock exchange.
Fees: Brokers charge a commission (brokerage fee) for each trade you execute.
Funding: You can deposit funds into your trading account to use for buying shares. You can also withdraw funds from successful sales.
Analogy: Think of it like your online banking account, but specifically for stock market transactions.
Demat Account:
Function: This account acts as a digital repository to hold your purchased shares in electronic form.
Process: You open a demat account with a depository participant (DP), a custodian who electronically holds and manages your securities.
Storage: Similar to how a bank holds your money electronically, a demat account holds your shares electronically, eliminating the need for physical certificates.
Trading: Shares can be bought and sold directly from your demat account.
Delivery: You can choose to take delivery of your shares in physical form if needed (though this is less common nowadays).
Analogy: Think of it like a safe deposit box, but for your electronic shares.
Why you need both:
You cannot buy shares directly into your bank account. You need a trading account to place buy and sell orders.
Shares purchased are then deposited into your demat account for safekeeping.
Benefits of Trading & Demat Accounts:
Convenient Trading: Allows you to easily buy and sell shares electronically.
Safekeeping: Demat accounts offer a secure way to hold your shares.
Delivery Option: You can choose to take physical possession of your shares if desired.
Investment Opportunity: Opens doors to potentially profiting from the stock market.
Risks to Consider:
Market Volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate, leading to potential losses.
Investment Knowledge: Understanding the market and making informed decisions is crucial.
Broker Selection: Choosing a reputable and reliable broker is important.
DEMAT &TRADING അക്കൗണ്ട്
ട്രേഡിംഗ് & ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട്
ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ വ്യാപാരം നടത്താൻ നിങ്ങൾക്ക് രണ്ട് തരം അക്കൗണ്ടുകൾ ആവശ്യമാണ്: ട്രേഡിംഗ് അക്കൗണ്ടും ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടും.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് അക്കൗണ്ട്:
ഓഹരി വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനും ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന അക്കൗണ്ട്.
ഒരു ബ്രോക്കറുടെ സഹായത്തോടെയാണ് ട്രേഡിംഗ് അക്കൗണ്ട് തുറക്കുന്നത്.
ഓരോ ട്രേഡിനും ബ്രോക്കറേജ് ഈടാക്കും.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് അക്കൗണ്ടിൽ നിന്ന് പണം നിക്ഷേപിക്കാനും പിൻവലിക്കാനും സാധിക്കും.
ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട്:
ഓഹരികൾ ഡീമാറ്റ് രൂപത്തിൽ സൂക്ഷിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന അക്കൗണ്ട്.
ഒരു ഡിപോസിറ്ററിയുടെ സഹായത്തോടെയാണ് ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട് തുറക്കുന്നത്.
ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിൽ നിന്ന് ഓഹരികൾ വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനും സാധിക്കും.
ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിൽ നിന്ന് ഓഹരികൾ ഡീലിവറിക്ക് എടുക്കാനും സാധിക്കും.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് & ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട് തുറക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള നടപടിക്രമങ്ങൾ:
ഒരു ബ്രോക്കറെ തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുക.
ബ്രോക്കറുടെ വെബ്സൈറ്റിൽ നിന്നോ ഓഫീസിൽ നിന്നോ അക്കൗണ്ട് തുറക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള അപേക്ഷാ ഫോം പൂരിപ്പിക്കുക.
ആവശ്യമായ രേഖകൾ സമർപ്പിക്കുക.
അക്കൗണ്ട് തുറക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഫീസ് അടയ്ക്കുക.
അക്കൗണ്ട് സജീവമാക്കിയ ശേഷം, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ട്രേഡിംഗ് ആരംഭിക്കാം.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് & ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിന്റെ നേട്ടങ്ങൾ:
ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ എളുപ്പത്തിൽ വ്യാപാരം നടത്താൻ സാധിക്കും.
ഓഹരികൾ സുരക്ഷിതമായി സൂക്ഷിക്കാൻ സാധിക്കും.
ഓഹരികൾ ഡീലിവറിക്ക് എടുക്കാൻ സാധിക്കും.
ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ നിന്നുള്ള വരുമാനം നേടാൻ സാധിക്കും.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് & ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ടിന്റെ അപകടസാധ്യതകൾ:
ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ അപകടസാധ്യത ഉൾപ്പെട്ടിരിക്കുന്നു.
ഓഹരി വിലയിലെ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകൾ കാരണം നഷ്ടം സംഭവിക്കാം.
തെറ്റായ നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ കാരണം നഷ്ടം സംഭവിക്കാം.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് & ഡീമാറ്റ് അക്കൗണ്ട് തുറക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് നിങ്ങൾ:
ഓഹരി വിപണിയെക്കുറിച്ച് നന്നായി മനസ്സിലാക്കണം.
നിങ്ങളുടെ റിസ്ക് ടോളറൻസ് നിർണ്ണയിക്കണം.
നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ നിർണ്ണയിക്കണം.
ഒരു നല്ല ബ്രോക്കറെ തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കണം.
Market Participants in stock market
Investors: Retail investors, institutional investors (mutual funds, insurance companies, foreign institutional investors).
Market intermediaries: Brokers, sub-brokers, depository participants, clearing corporations.
which Financial Instruments are Traded in stock market?
Equity shares: Common stocks listed on stock exchanges.
Derivatives: Futures and options contracts on stocks, indices, and commodities.
Bonds and Debentures: Fixed-income securities issued by corporations and government entities.
Mutual Funds: Pooled investment vehicles managed by asset management companies.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): Funds that track indices and trade on stock exchanges.
Market Indices:
Nifty 50: Benchmark index of NSE, comprising 50 large-cap stocks.
Sensex: Benchmark index of BSE, comprising 30 large-cap stocks.
Other indices: Sectoral indices (Bank Nifty, Nifty IT, etc.) and thematic indices.
Trading Mechanism:
Trading sessions: Pre-open session, normal trading session, and post-closing session.
Order types: Market orders, limit orders, stop-loss orders, etc.
Settlement process: T+2 settlement cycle for equity trades.
Market Regulations and Compliance:
Insider trading regulations.
Corporate governance norms.
Listing requirements for companies.
Market Trends and Analysis:
Fundamental analysis: Evaluating companies based on financial statements, industry trends, and economic factors.
Technical analysis: Using price charts and technical indicators to forecast price movements.
Sentiment analysis: Monitoring market sentiment through news, social media, and other sources.
Investment Strategies and Risk Management:
Long-term investing vs. short-term trading.
Diversification strategies.
Risk management techniques (stop-loss orders, portfolio hedging, etc.).
Recent Developments and Future Outlook:
Introduction of new products and technologies (e.g., algorithmic trading, blockchain-based solutions).
Government policies and reforms impacting the market.
Growth prospects and challenges facing the Indian stock market.
define equity shares with example
Equity shares, also known as common stock, represent fractional ownership in a company. When you buy an equity share, you're essentially buying a tiny piece of the company itself. This ownership grants you certain rights and comes with some potential benefits and risks.
Here's a breakdown of key points about equity shares:
Ownership:
Each equity share represents a unit of ownership in the company. The more shares you own, the larger your ownership stake.
Rights of Equity Shareholders:
Voting rights: In most cases, equity shareholders have the right to vote on important company decisions, such as electing board members or approving major acquisitions. The number of votes typically corresponds to the number of shares owned. (Some companies might have different classes of shares with varying voting rights.)
Profit sharing (Dividends): Companies may distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends. However, dividends are not guaranteed and are at the discretion of the company's board of directors.
Capital appreciation: If the company performs well and its stock price increases, you can potentially profit by selling your shares at a higher price than you bought them for.
Example:
Imagine a company called "Bake Me Happy" decides to go public and issue 1 million equity shares. You invest in the IPO (Initial Public Offering) and buy 1,000 shares. This means you now own 0.1% of Bake Me Happy (1,000 shares / 1,000,000 total shares).
Voting Rights: As a shareholder, you have the right to vote on company matters at shareholder meetings. The number of votes you have will likely be proportional to your 1,000 shares.
Dividends: If Bake Me Happy has a profitable year, they might choose to distribute some of those profits to shareholders as dividends. The amount you receive would depend on the total dividend declared by the company and the number of shares you hold.
Capital Appreciation: If Bake Me Happy's business expands and their stock price goes up, the value of your 1,000 shares will also increase. You could then potentially sell your shares for a profit.
Important to Remember:
Equity shares come with inherent risks. The company's performance can directly impact the value of your shares. If the company struggles financially, the share price could decline, and you might lose money if you sell your shares.
Equity shares are not like bonds and don't guarantee a fixed return. Unlike bondholders, shareholders are not guaranteed to receive dividends.
By understanding equity shares, you can make informed decisions about investing in companies and potentially benefit from their growth. However, it's crucial to be aware of the associated risks and conduct thorough research before investing.
ഓഹരി (Equity Shares) എന്താണ്?
ഓഹരി, ഒരു കമ്പനിയിലെ ഉടമസ്ഥതയുടെ ഏറ്റവും ചെറിയ യൂണിറ്റാണ്. ഒരു കമ്പനി ഓഹരികൾ പുറത്തിറക്കുമ്പോEquity shares എന്താണ്. ഉദാഹരണം സഹിതം വിശദമാക്കുകൾ, നിങ്ങൾ ഓഹരി വാങ്ങുമ്പോൾ, നിങ്ങൾ ആ കമ്പനിയിൽ ഒരു ചെറിയ ഓഹരി ഉടമയാകുന്നു. ഓഹരി ഉടമസ്ഥത നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ചില അവകാശങ്ങളും നേട്ടങ്ങളും നൽകുന്നു, അതേസമയം ചില അപകടസാധ്യതകളും ഉൾക്കൊള്ളുന്നു.
ഓഹരി ഉടമസ്ഥതയുടെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
വോട്ടവകാശം: ഓഹരി ഉടമകൾക്ക് സാധാരണയായി കമ്പനിയുടെ പ്രധാന തീരുമാനങ്ങളിൽ വോട്ട് ചെയ്യാനുള്ള അവകാശമുണ്ട്.
ലാഭവിഹിതം: കമ്പനി ലാഭം നേടുകയാണെങ്കിൽ, ഓഹരി ഉടമകൾക്ക് ലാഭവിഹിതം ലഭിക്കും.
മൂല്യവർദ്ധനവ്: കമ്പനി നന്നായി പ്രവർത്തിക്കുകയും ഓഹരി വില ഉയരുകയും ചെയ്യുകയാണെങ്കിൽ, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ഓഹരികൾ വിറ്റ് ലാഭം നേടാം.
ഉദാഹരണം:
"Bake Me Happy" എന്ന ഒരു കമ്പനി 10 ലക്ഷം ഓഹരികൾ പുറത്തിറക്കുന്നു എന്ന് കരുതുക. നിങ്ങൾ ഈ ഓഹരികളിൽ 1000 എണ്ണം വാങ്ങുന്നു. ഇതിനർത്ഥം നിങ്ങൾ Bake Me Happy-യിൽ 0.1% ഉടമസ്ഥാവകാശം നേടി എന്നാണ് (1000 ഓഹരികൾ / 10 ലക്ഷം ഓഹരികൾ).
വോട്ടവകാശം: ഓഹരി ഉടമ എന്ന നിലയിൽ, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് കമ്പനിയുടെ ഓഹരി ഉടമകളുടെ യോഗത്തിൽ വോട്ട് ചെയ്യാനുള്ള അവകാശമുണ്ട്. നിങ്ങളുടെ 1000 ഓഹരികൾക്ക് അനുസൃതമായി നിങ്ങൾക്ക് വോട്ട് ചെയ്യാൻ കഴിയും.
ലാഭവിഹിതം: Bake Me Happy ലാഭം നേടുകയും ലാഭവിഹിതം നൽകാൻ തീരുമാനിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുകയാണെങ്കിൽ, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ലാഭവിഹിതം ലഭിക്കും. ലഭിക്കുന്ന ലാഭവിഹിതം കമ്പനി നൽകുന്ന ലാഭവിഹിതത്തിന്റെയും നിങ്ങളുടെ ഓഹരികളുടെ എണ്ണത്തിന്റെയും അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിലായിരിക്കും.
മൂല്യവർദ്ധനവ്: Bake Me Happy-യുടെ ബിസിനസ്സ് വളരുകയും ഓഹരി വില ഉയരുകയും ചെയ്യുകയാണെങ്കിൽ, നിങ്ങളുടെ 1000 ഓഹരികളുടെ മൂല്യം വർദ്ധിക്കും. ഈ ഓഹരികൾ പിന്നീട് ലാഭത്തോടെ വിൽക്കാൻ നിങ്ങൾക്ക് സാധിക്കും.
ഓർത്തിരിക്കേണ്ട കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
ഓഹരികൾ അപകടസാധ്യതകൾ ഉൾക്കൊള്ളുന്നു. കമ്പനിയുടെ പ്രകടനം ഓഹരി വിലയെ നേരിട്ട് ബാധിക്കും. കമ്പനിക്ക് പ്രശ്നങ്ങൾ നേരിടുകയാണെങ്കിൽ, ഓഹരി വില കുറയുകയും നിങ്ങൾ ഓഹരികൾ വിൽക്കുകയാണെങ്കിൽ നഷ്ടം സംഭവിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യും.
ഓഹരികൾ ഒരു ബോണ്ട് പോലെയല്ല, ഒരു നിശ്ചിത വരുമാനം ഉറപ്പുനൽകുന്നില്ല
derivatives in indian stock market with example
Derivatives in the Indian Stock Market: Understanding Financial Contracts
The Indian stock market offers a variety of investment options, and derivatives are a unique category of financial instruments. Unlike stocks that represent ownership in a company, derivatives derive their value from an underlying asset, which can be a stock, index, commodity, currency, or even interest rates.
Here's a breakdown of derivatives in the Indian context:
What are Derivatives?
Contracts between two parties that derive their value from the future performance of an underlying asset.
Used for various purposes: hedging existing investments, speculating on price movements, or leveraging positions to potentially amplify gains (or losses).
Types of Derivatives in India:
Futures Contracts:
Agreement to buy or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price on a specific future date.
Example: You enter a futures contract to buy 100 shares of Reliance Industries at Rs. 2,500 three months from now. Regardless of the market price in three months, you're obligated to buy at Rs. 2,500.
Options Contracts:
Provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) an underlying asset at a certain price by a specific date.
Example: You buy a call option for 100 shares of Infosys with a strike price of Rs. 1,500 expiring in two months. This gives you the right, but not the obligation, to buy those shares at Rs. 1,500 within two months, even if the market price is higher.
Benefits of Derivatives:
Hedging: Allows investors to protect their existing holdings from price fluctuations.
Speculation: Enables investors to potentially profit from anticipated price movements in the underlying asset.
Leverage: Amplifies potential gains (and losses) by using a smaller amount of capital compared to buying the underlying asset directly.
Risks of Derivatives:
Complexity: Derivatives can be complex instruments, and a thorough understanding is crucial before investing.
High Risk: The potential for significant losses exists due to leverage and unpredictable market movements.
Margin Requirements: May require upfront margin deposits to enter into derivative contracts.
Regulation in India:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates derivatives trading in India.
SEBI ensures fair and transparent trading practices and protects investor interests.
Example: Hedging with Futures
Imagine you own 100 shares of SBI at Rs. 500 per share. You're concerned about a potential price drop. To hedge this risk, you could enter a futures contract to sell 100 SBI shares at Rs. 500 three months from now.
If the price goes down: You can still sell your shares at the predetermined price of Rs. 500 using the futures contract, limiting your losses.
If the price goes up: You can choose to forgo the futures contract and sell your shares at the higher market price, profiting from the increase.
Remember: Derivatives are powerful tools but come with inherent risks. Conduct thorough research, understand the risks involved, and consider your risk tolerance before venturing into derivative trading.
DERIVATIVES എന്താണെന്നു ഉദാഹരണം സഹിതം വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിലെ ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സ്: സാമ്പത്തിക കരാറുകൾ മനസ്സിലാക്കുക
ഓഹരികളിൽ ഉടമസ്ഥത നേടാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്ന ഓഹരികൾക്ക് പുറമെ, ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റ് വ്യത്യസ്തമായ നിക്ഷേപ ഓപ്ഷനുകളും വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സ് എന്നറിയപ്പെടുന്ന സാമ്പത്തിക ഉപകരണങ്ങളുടെ ഒരു വിഭാഗം ഇതിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു. ഓഹരികൾ പോലെ കമ്പനിയിലെ ഉടമസ്ഥത പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നതിനുപകരം, ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സിന്റെ മൂല്യം ഒരു അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തിയിൽ നിന്നാണ് ഉരുത്തിരിയുന്നത്. ഓഹരി, സൂചിക, കച്ചവസ്തു, നാണയം, പലിശ നിരക്ക് എന്നിവ ഇതിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു.
ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സ് എന്താണ്?
ഒരു അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തിയുടെ ഭാവി പ്രകടനത്തെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി രണ്ട് കക്ഷികൾ തമ്മിലുള്ള കരാർ.
നിലവിലുള്ള നിക്ഷേപങ്ങൾ ഹെഡ്ജ് ചെയ്യാനും, വിലയിലെ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകളിൽ നിന്ന് സാമ്പത്തിക നേട്ടം നേടാനും, ലാഭം (അല്ലെങ്കിൽ നഷ്ടം) വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കാൻ സ്ഥാനം ലിവറേജ് ചെയ്യാനും ഉപയോഗിക്കാം.
ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സിന്റെ തരങ്ങൾ:
ഫ്യൂച്ചേഴ്സ് കരാറുകൾ:
ഒരു നിശ്ചിത ഭാവി തീയതിയിൽ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത വിലയ്ക്ക് ഒരു അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തി വാങ്ങാനോ വിൽക്കാനോ ഉള്ള കരാർ.
ഉദാഹരണം: മൂന്ന് മാസത്തിന് ശേഷം 2,500 രൂപയ്ക്ക് 100 റിലയൻസ് ഇൻഡസ്ട്രീസ് ഓഹരികൾ വാങ്ങാൻ നിങ്ങൾ ഒരു ഫ്യൂച്ചേഴ്സ് കരാറിൽ പ്രവേശിക്കുന്നു. മൂന്ന് മാസത്തിന് ശേഷം വിപണി വില എന്തുതന്നെയായാലും, നിങ്ങൾ 2,500 രൂപയ്ക്ക് വാങ്ങാൻ നിർബന്ധിതരാണ്.
ഓപ്ഷൻസ് കരാറുകൾ:
ഒരു നിശ്ചിത തീയതിക്ക് മുമ്പ് ഒരു നിശ്ചിത വിലയ്ക്ക് ഒരു അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തി വാങ്ങാനുള്ള (കോൾ ഓപ്ഷൻ) അല്ലെങ്കിൽ വിൽക്കാനുള്ള (പുട്ട് ഓപ്ഷൻ) അവകാശം നൽകുന്നു.
ഉദാഹരണം: രണ്ട് മാസത്തിനുള്ളിൽ 1,500 രൂപയുടെ സ്ട്രൈക്ക് വിലയുള്ള 100 ഇൻഫോസിസ് ഓഹരികൾക്കുള്ള ഒരു കോൾ ഓപ്ഷൻ നിങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങുന്നു. ഇത് രണ്ട് മാസത്തിനുള്ളിൽ 1,500 രൂപയ്ക്ക് ഓഹരികൾ വാങ്ങാനുള്ള അവകാശം നിങ്ങൾക്ക് നൽകുന്നു, വിപണി വില എത്രത്തോളം ഉയർന്നാലും.
DERIVATIVES ന്റെ ഗുണങ്ങളും ദോഷങ്ങളും
ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
ഹെഡ്ജിംഗ്: നിലവിലുള്ള നിക്ഷേപങ്ങൾ വിലയിലെ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകളിൽ നിന്ന് സംരക്ഷിക്കാൻ നിക്ഷേപകരെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു.
ഊഹക്കച്ചവടം: അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തിയുടെ വിലയിലെ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകളിൽ നിന്ന് സാമ്പത്തിക നേട്ടം നേടാൻ നിക്ഷേപകരെ പ്രാപ്തരാക്കുന്നു.
ലിവറേജ്: കുറഞ്ഞ മൂലധനം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് ലാഭം (അല്ലെങ്കിൽ നഷ്ടം) വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കാൻ നിക്ഷേപകരെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു.
വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം: നിക്ഷേപ പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരിക്കാനുള്ള ഒരു മാർഗം നൽകുന്നു.
വരുമാനം സൃഷ്ടിക്കുക: പ്രീമിയം വിൽക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ വരുമാനം സൃഷ്ടിക്കാൻ ഓപ്ഷൻസ് ഉപയോഗിക്കാം.
ദോഷങ്ങൾ:
സങ്കീർണ്ണത: ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സ് സങ്കീർണ്ണമായ ഉപകരണങ്ങളാകാം, അവയിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിന് മുമ്പ് നന്നായി മനസ്സിലാക്കേണ്ടതുണ്ട്.
ഉയർന്ന അപകടസാധ്യത: ലിവറേജ് കാരണം കാര്യമായ നഷ്ടം സംഭവിക്കാനുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്.
മാർജിൻ ആവശ്യകതകൾ: ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് കരാറുകളിൽ പ്രവേശിക്കുന്നതിന് മുൻകൂർ മാർജിൻ നിക്ഷേപം ആവശ്യമായി വന്നേക്കാം.
വിപണി 操纵: വിപണി 操纵 ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് വിപണികളിൽ കൂടുതൽ സാധാരണമാണ്.
നിയന്ത്രണം: ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് വിപണികൾ സർക്കാർ നിയന്ത്രണം വിധേയമാണ്, ഇത് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് അധിക ബാധ്യതകൾ സൃഷ്ടിച്ചേക്കാം.
ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സ് ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് ശ്രദ്ധിക്കേണ്ട കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
നിങ്ങളുടെ റിസ്ക് ടോളറൻസ് വിലയിരുത്തുക.
ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സിന്റെ സങ്കീർണ്ണത മനസ്സിലാക്കുക.
ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ്സിന്റെ ഗുണങ്ങളും ദോഷങ്ങളും വിശദമായി പഠിക്കുക.
നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് വിപണി ഗവേഷണം നടത്തുക.
ഒരു സാമ്പത്തിക ഉപദേഷ്ടാവിന്റെ സഹായം തേടുക.
IMPORTANT DERIVATIVES FINANCIAL MATERIALS IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET
In the Indian stock market, derivatives contracts are available for a wide range of underlying assets, and financial materials are definitely one of the important sectors. Here's a breakdown of the key players:
Financial Material Derivatives:
Equity Derivatives: These are the most common type of derivatives based on financial materials. They include futures and options contracts on individual stocks of companies in the financial sector. This sector encompasses banks, insurance companies, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), and other financial institutions.
Examples:
Futures on Reliance Industries: You can enter a contract to buy or sell Reliance Industries stock at a predetermined price on a specific future date.
Options on HDFC Bank: You can buy a call option to potentially profit if HDFC Bank's stock price goes up, or a put option to hedge your holdings if the price goes down.
Commodity Derivatives:
While less common, derivatives also exist for certain commodities relevant to the financial sector. For instance, there could be futures contracts on gold or silver, which are sometimes used by financial institutions for hedging purposes.
Why are Financial Material Derivatives Important?
Hedging: Financial institutions and investors can use derivatives to hedge their exposure to fluctuations in stock prices or commodity prices related to finance.
Speculation: Traders can use derivatives to speculate on the future movement of stock prices or commodity prices in the financial sector, potentially profiting if their predictions are correct.
Market Efficiency: Derivatives can contribute to a more efficient market by allowing for price discovery and risk management.
Important Note:
The specific financial materials available for derivatives trading can vary depending on the exchange and regulations. It's crucial to check with your broker or exchange for the latest offerings.
Additional Sectors with Important Derivatives:
While financial materials are a significant sector, derivatives are also widely used in other sectors of the Indian stock market, including:
Commodities: Derivatives on agricultural products, metals, and energy resources.
Equity Indices: Contracts based on major stock market indices like Nifty 50 and Sensex.
Currency Derivatives: Contracts based on foreign exchange rates.
By understanding the different types of derivatives and the sectors they cover, you can gain a broader perspective on the Indian financial markets.
NIFTY OPTIONS TRADING
Nifty Options Trading: A Guide to Speculating on the Indian Stock Market Index
Nifty options trading involves using options contracts to speculate on the future movement of the Nifty 50 index, a benchmark stock market index in India. It allows traders to take calculated risks and potentially profit from both upward and downward movements of the index, unlike buying stocks where you only profit if the stock price goes up.
Here's a breakdown of Nifty options trading:
Understanding Options Contracts:
Options contracts grant the right, but not the obligation, to buy (call option) or sell (put option) a specific number of units (lots) of the Nifty 50 index at a predetermined price (strike price) by a certain expiry date.
You don't own the underlying index itself when you buy an option, unlike buying stocks.
How Nifty Options Trading Works:
Choosing a Direction: Decide whether you think the Nifty 50 index will go up (bullish) or down (bearish).
Selecting Option Type:
Call Option: Purchase a call option if you believe the index will rise. Profits are potentially unlimited, but there's a premium cost to pay upfront.
Put Option: Purchase a put option if you believe the index will fall. Profits are capped at the difference between the strike price and the index price at expiry, but there's a premium cost upfront.
Setting Strike Price: Choose a strike price that aligns with your prediction of the index movement.
Expiry Date: Select an expiry date that suits your trading strategy (e.g., weekly, monthly). Options lose value as they approach expiry.
Example:
You think the Nifty 50 index will rise. You buy a call option with a strike price of 17,000 and an expiry date two months from now. The premium for this option is Rs. 100 per lot.
If the Nifty 50 index goes up to 18,000 by expiry, you can exercise your option to buy the index at 17,000 and immediately sell it at the market price of 18,000, profiting Rs. 1000 per lot (excluding brokerage fees).
Benefits of Nifty Options Trading:
Potential for High Returns: Leverage the potential for significant profits if your directional prediction is correct.
Limited Risk: Your maximum loss is limited to the option premium paid, unlike buying stocks where losses can be substantial.
Profiting from Downward Markets: Put options allow you to profit even if the market falls.
Risks of Nifty Options Trading:
Time Decay: Option contracts lose value over time (time decay), even if the index stays flat.
Complexity: Options trading requires a good understanding of market dynamics and option pricing models.
Potential for Loss: If your prediction is wrong, you lose the entire option premium.
Who Should Consider Nifty Options Trading?
Nifty options trading is suitable for experienced traders comfortable with higher risks and who can devote time to market analysis. It's not recommended for beginners due to its complexity.
Remember: Options trading can be a powerful tool, but it comes with inherent risks. Conduct thorough research, understand the risks
MARKET CAPITALISATION
Market capitalization, often abbreviated as market cap, is a key metric used to determine the total market value of a publicly traded company. It essentially reflects the company's overall size and worth as perceived by the stock market.
Here's how market cap is calculated:
Market Cap = Share Price per Share * Number of Outstanding Shares
Share Price per Share: This is the current market price of a single share of the company's common stock. It fluctuates throughout the trading day based on supply and demand.
Number of Outstanding Shares: This represents the total number of shares of a company's common stock that are currently held by investors.
For example:
If a company's stock price is ₹100 per share and there are 10 million outstanding shares, the market capitalization would be ₹1,000,000,000 (₹100/share * 10,000,000 shares).
Importance of Market Capitalization:
Company Size: Market cap is a simple and widely used indicator of a company's relative size compared to other publicly traded companies. Generally, companies with higher market caps are considered larger and more established.
Investment Decisions: Investors often use market cap to categorize companies into different investment groups, such as large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks. This helps them choose investments based on their risk tolerance and growth expectations.
Industry Benchmarking: By comparing the market cap of companies within the same industry, investors can assess a company's performance relative to its competitors.
Things to Consider About Market Cap:
Market Cap Doesn't Reflect Everything: While market cap is a valuable metric, it doesn't necessarily reflect a company's profitability, future potential, or financial health. Other financial ratios and metrics should also be considered for a comprehensive investment analysis.
Market Fluctuations: Since market cap is based on the current stock price, it can fluctuate significantly based on market movements.
Overall, market capitalization is a crucial concept for understanding the size and worth of publicly traded companies. It plays a significant role in investment decisions and overall market analysis.
MARKET CAPITALISATION എന്താണ് വിശദമാക്കുക
വിപണി മൂലധനം, പലപ്പോഴും മാർക്കറ്റ് ക്യാപ് [market cap] എന്ന് ചുരുക്കി പറയുന്നത്, പൊതുവായി വ്യാപാരം ചെയ്യുന്ന ഒരു കമ്പനിയുടെ മൊത്തം വിപണി മൂല്യം നിർണ്ണയിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന ഒരു പ്രധാന മാനദണ്ഡമാണ്. ഇത് ഓഹരി വിപണി കമ്പനിയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള വലിപ്പവും മൂല്യവും ഓഹരി വിപണി എങ്ങനെ കാണുന്നു എന്നതിന്റെ പ്രതിഫലനമാണ്.
വിപണി മൂലധനം എങ്ങനെ കണക്കാക്കുന്നു?
വിപണി മൂലധനം = ഓഹരിയുടെ വില * നിലവിലുള്ള ഓഹരികളുടെ എണ്ണം
ഓഹരിയുടെ വില: ഇത് കമ്പനിയുടെ സാധാരണ ഓഹരിയുടെ ഒരു ഓഹരിയുടെ നിലവിലെ വിപണി വിലയാണ്. ഓഹരി വിപണി ദിവസം മുഴുവന വിതരണത്തിന്റെയും ഡിമാൻഡിന്റെയും അടിസ്ഥാനത്തിൽ ഇത് വ്യത്യാസപ്പെടുന്നു.
നിലവിലുള്ള ഓഹരികളുടെ എണ്ണം: ഇത് നിലവിൽ നിക്ഷേപകർ കൈവശം വച്ചിരിക്കുന്ന കമ്പനിയുടെ സാധാരണ ഓഹരികളുടെ മൊത്തം എണ്ണത്തെ 나타ക്കുന്നു.
ഉദാഹരണത്തിന്:
ഒരു കമ്പനിയുടെ ഓഹരി വില ₹100 ആണെങ്കിൽ, 10 ദശലക്ഷം നിലവിലുള്ള ഓഹരികളുണ്ടെങ്കിൽ, വിപണി മൂലധനം ₹1,000,000,000 (₹100/ഓഹരി * 10,000,000 ഓഹരികൾ) ആയിരിക്കും.
വിപണി മൂലധനത്തിന്റെ പ്രാധാന്യം:
കമ്പനിയുടെ വലിപ്പം: മറ്റ് പൊതുവായി വ്യാപാരം ചെയ്യുന്ന കമ്പനികളുമായി താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തുമ്പോൾ കമ്പനിയുടെ അപേക്ഷിക വലിപ്പത്തിന്റെ ഒരു ലളിതവും വ്യാപകമായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നതുமான സൂചകമാണ് വിപണി മൂലധനം. സാധാരണയായി, ഉയർന്ന വിപണി മൂലധനമുള്ള കമ്പനികളെ വലുതയുള്ളതും കൂടുതൽ സ്ഥാപിതവുമായവയായി കണക്കാക്കുന്നു.
നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ: നിക്ഷേപകർ പലപ്പോഴും വിപണി മൂലധനം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് കമ്പനிகളെ ലാർജ് കാപ്, മിഡ് കാപ്, സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ പോലുള്ള വിവിധ നിക്ഷേപ ഗ്രൂപ്പുകളായി തരംതിരിക്കുന്നു. ഇത് അവരുടെ അപകടസാധ്യത സഹിഷ്ണുതയെയും വളർച്ച പ്രതീക്ഷകളെയും അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി നിക്ഷേപങ്ങൾ OFDbഅനുയോജ്യപ്പെടുത്താൻ [choose] അവരെ സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
വ്യവസായ ബെഞ്ച്മാർക്കിംഗ്: ഒരേ വ്യവസായത്തിലെ കമ്പനികളുടെ വിപണി മൂലധനം താരതമ്യം ചെയ്യുന്നതിലൂടെ, നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഒരു കമ്പനിയുടെ പ്രകടനം അതിന്റെ മത്സരാർഥികളുടെ അപേക്ഷയിൽ വിലയിരുത്താൻ കഴിയും.
NIFTY FIFTY INDEX
The Nifty 50 index doesn't directly hold specific stocks, but it represents the performance of 50 of the largest companies listed on the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE). These companies are chosen based on various factors like market capitalization (total market value) and liquidity (ease of buying and selling).
While the Nifty 50 doesn't denote individual stocks, the index itself is constructed by considering the weightage of these 50 companies. This weightage reflects the company's market capitalization relative to the total market capitalization of all 50 companies in the Nifty 50.
Therefore, there aren't specific "important indexes" within Nifty 50. However, the Nifty 50 itself is an important indicator of the overall performance of the Indian stock market.
Here's a breakdown of how Nifty 50 reflects the market:
Market Capitalization: Companies with a larger market cap have a greater influence on the Nifty 50's movement. For example, Reliance Industries, typically having a high market cap, will impact the Nifty 50 more than a smaller company.
Sectoral Representation: The 50 companies in the Nifty 50 are spread across various sectors like financials, IT, energy, FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods), and others. This diversification provides a good overview of the health of different sectors of the Indian economy.
Understanding the composition of the Nifty 50 can be helpful, but it doesn't replace the index itself. The Nifty 50 remains the key indicator for market performance.
Additional Resources:
Nifty 50 Index on NSE website: https://www.nseindia.com/
List of Nifty 50 companies: https://www.nseindia.com/products-services/indices-nifty50-index
Nifty fifty index എന്താണെന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിലെ നിഫ്റ്റി ഫിഫ്റ്റി സൂചിക: ഒരു വിശദീകരണം
നിഫ്റ്റി ഫിഫ്റ്റി സൂചിക, നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (NSE) ൽ ലിസ്റ്റുചെയ്തിരിക്കുന്ന 50 വലിയ കമ്പനികളുടെ പ്രകടനം പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുന്ന ഒരു പ്രധാന സൂചികയാണ്. വിപണി മൂലധനം (total market value) , ദ്രാവകത (liquidity) പോലുള്ള ഘടകങ്ങളെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കിയാണ് ഈ കമ്പനികളെ തിരഞ്ഞെടുക്കുന്നത്.
ഓരോ കമ്പനിയും നിഫ്റ്റി 50 ൽ വഹിക്കുന്ന ഭാരം (weightage) , അതിന്റെ വിപണി മൂലധനവും 50 ൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്ന എല്ലാ കമ്പനികളുടെയും മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള വിപണി മൂലധനവും തമ്മിലുള്ള അനുപാതം അനുസരിച്ചിരിക്കും.
നിഫ്റ്റി ഫിഫ്റ്റി സൂചികയുടെ പ്രാധാന്യം:
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ ആരോഗ്യം അളക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഒരു പ്രധാന സൂചകം: നിഫ്റ്റി 50 ന്റെ ചലനം ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള ദിശാബോധം സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
വ്യത്യസ്ത സെക്ടറുകളുടെ പ്രകടനം വിലയിരുത്താൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു: 50 കമ്പനികളും ധനകാര്യം, ഐടി, ഊർജ്ജം, FMCG (Fast Moving Consumer Goods) തുടങ്ങിയ വിവിധ സെക്ടറുകളിൽ നിന്നുള്ളതാണ്.
നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ എടുക്കാൻ സഹായകരം: നിഫ്റ്റി 50 ൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്ന കമ്പനികളിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കാൻ താൽപ്പര്യമുള്ള നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഈ സൂചിക ഒരു നല്ല തുടക്കം നൽകും.
നിഫ്റ്റി ഫിഫ്റ്റി സൂചികയെക്കുറിച്ച് കൂടുതൽ മനസ്സിലാക്കാൻ:
NSE വെബ്സൈറ്റിലെ നിഫ്റ്റി 50 സൂചിക: https://www.nseindia.com/products-services/indices-nifty50-index
നിഫ്റ്റി 50 ൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്ന കമ്പനികളുടെ പട്ടിക: [അസാധുവായ URL നീക്കം ചെയ്തു]
നിഫ്റ്റി ഫിഫ്റ്റി സൂചിക, ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ പ്രകടനം വിലയിരുത്താൻ സഹായിക്കുന്ന ഒരു പ്രധാന ഉപകരണമാണ്. ഈ സൂചികയെക്കുറിച്ച് നന്നായി മനസ്സിലാക്കുന്നത് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് അവരുടെ നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ മെച്ചപ്പെടുത്താൻ സഹായിക്കും.
BANK NIFTY
Bank Nifty Explained: A Benchmark for India's Banking Sector
The Bank Nifty, also known as Nifty Bank, is a stock market index that tracks the performance of the banking sector in India. It's a crucial benchmark for investors and analysts to gauge the health and direction of this vital sector of the Indian economy.
Composition of Bank Nifty:
Unlike the Nifty 50, which tracks the top 50 companies across sectors, Bank Nifty focuses specifically on the banking sector.
It comprises the 12 largest and most liquid banking stocks listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India.
These banks can be public sector banks (owned by the government) or private sector banks.
Why is Bank Nifty Important?
Provides a Snapshot of Banking Sector Health: The Bank Nifty reflects the overall performance of the banking sector. An upswing in the index indicates a positive sentiment towards banking stocks, while a decline suggests a cautious outlook.
Influences Investment Decisions: Investors and fund managers use Bank Nifty to make informed decisions about investing in banking stocks or banking sector-focused mutual funds and ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds).
Underlying Asset for Derivatives: Bank Nifty serves as the underlying asset for derivative instruments like futures and options contracts. These allow traders to speculate on the future movement of the banking sector's performance.
Benefits of Tracking Bank Nifty:
Early Warning Signs: By monitoring Bank Nifty, investors can identify potential risks or opportunities in the banking sector before they become apparent in individual bank stocks.
Benchmarking Performance: Investors holding banking stocks or banking sector funds can compare their performance to the Bank Nifty to assess their relative returns.
Understanding Market Sentiment: The Bank Nifty can provide insights into the overall market sentiment towards the banking sector, helping investors make informed decisions.
Things to Remember About Bank Nifty:
More Volatile Than Nifty 50: Since Bank Nifty focuses on a single sector, it can be more volatile than the broader Nifty 50 index, which is diversified across sectors.
Doesn't Represent the Entire Banking Sector: While Bank Nifty includes the 12 largest banks, it doesn't encompass every bank in India. Smaller banks may not necessarily follow the same trends as the Bank Nifty.
Overall, the Bank Nifty is a valuable tool for investors and market participants to understand the health and direction of the Indian banking sector. By tracking its performance and considering the associated risks and benefits, you can make more informed investment decisions related to the banking sector.
Bank nifty എന്താണെന്നു വിശദമാക്കുക
ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി: ഇന്ത്യയുടെ ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ ഒരു ബെഞ്ച്മാർക്ക്
ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി, അഥവാ നിഫ്റ്റി ബैंक, ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ പ്രകടനം ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്ന ഒരു സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റ് സൂചികയാണ്. ഇന്ത്യൻ സമ്പദ്व्यവസ്ഥയുടെ ഈ പ്രധാന മേഖലയുടെ ആരോഗ്യവും ദിശാബോധവും അളക്കുന്നതിന് നിക്ഷേപകർക്കും വിശകലന വിദഗ്ധർക്കും വേണ്ടിയുള്ള ഒരു നിർണായക ബെഞ്ച്മാർക്കാണിത്.
ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റിയുടെ ഘടന:
എല്ലാ സെക്ടറുകളിലുമുള്ള ടോപ്പ് 50 കമ്പനികളെ ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്ന നിഫ്റ്റി 50 ൽ നിന്ന് വ്യത്യസ്തമായി, ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി പ്രത്യേകിച്ച് ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയിൽ ശ്രദ്ധ കേന്ദ്രീകരിക്കുന്നു.
നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (NSE) യിൽ ലിസ്റ്റുചെയ്തിരിക്കുന്ന 12 ഏറ്റവും വലുതയുള്ളതും ഏറ്റവും ദ്രവ്യതയുള്ളതുമായ ബാങ്കിംഗ് ഓഹരികളാണ് ഇതിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നത്.
ഈ ബാങ്കുകൾ പൊതുമേഖലാ ബാങ്കുകളോ (സർക്കാർ ഉടമസ്ഥതയിലുള്ളവ) അല്ലെങ്കിൽ സ്വകാര്യ ബാങ്കുകളോ ആകാം.
ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടത് എന്തുകൊണ്ട്?
ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ ആരോഗ്യത്തെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള വിവരങ്ങൾ നൽകുന്നു: ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള പ്രകടനം പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. സൂചികയിലെ വർദ്ധനവ് ബാങ്കിംഗ് ഓഹരികളോടുള്ള പോസിറ്റീവ് വികാരത്തെയും കുറവ് ഈ മേഖലയോടുള്ള ജാഗ്രതയെയും സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങളെ സ്വാധീനിക്കുന്നു: നിക്ഷേപകരും ഫണ്ട് മാനേജർമാരും ബാങ്കിംഗ് ഓഹരികളിലോ ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലാ കേന്ദ്രീകൃത മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകളിലോ ETF-കളിലോ (എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ട്രേഡഡ് ഫണ്ടുകൾ) നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള വിവരമുള്ള തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ എടുക്കാൻ ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
ഉപകരണങ്ങളുടെ അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തി: ഭാവികരാറുകൾ, ഓപ്ഷൻ കരാറുകൾ പോലുള്ള ഡെറിവേറ്റീവ് ഉപകരണങ്ങൾക്കുള്ള അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തിയായി ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു. ഇവ ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ പ്രകടനത്തിന്റെ ഭാവി ചലനങ്ങളിൽ ഊഹക്കച്ചവടം നടത്താൻ വ്യാപാരികളെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു.
ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്നതിന്റെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
നേരത്തെയുള്ള മുന്നറിയിപ്പ് സൂചനകൾ: ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി നിരീക്ഷിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ, നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് വ്യക്തിഗത ബാങ്ക് ഓഹരികളിൽ പ്രകടമാകുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയിലെ സാധ്യതയുള്ള അപകടസാധ്യതകളോ അവസരങ്ങളോ തിരിച്ചറിയാൻ കഴിയും.
പ്രകടനം ബെഞ്ച്മാർക്ക് ചെയ്യുക: ബാങ്കിംഗ് ഓഹരികൾ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലാ ഫണ്ടുകൾ കൈവശമുള്ള നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് അവരുടെ ആപേക്ഷിക വരുമാനം വിലയിരുത്താൻ ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റിയുമായി അവരുടെ പ്രകടനം താരതമ്യം ചെയ്യാൻ കഴിയും.
വിപണി വികാരം മനസ്സിലാക്കുക: ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയോടുള്ള വിപണിയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള വികാരത്തെക്കുറിച്ച് ഉൾക്കാഴ്ച നൽകാൻ ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റിക്ക് കഴിയും, ഇത് നിക്ഷേപകരെ വിവരമുള്ള തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ എടുക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കും.
ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുമ്പോൾ ശ്രദ്ധിക്കേണ്ട കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
നിഫ്റ്റി 50 നെക്കാൾ വോളിറ്റൈൽ: ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി ഒരു സെക്ടറിൽ മാത്രം ശ്രദ്ധ കേന്ദ്രീകരിക്കുന്നതിനാൽ, വിവിധ സെക്ടറുകളിൽ വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരിച്ചിരിക്കുന്ന നിഫ്റ്റി 50 സൂചികയെക്കാൾ ഇത് കൂടുതൽ വോളിറ്റൈൽ ആകാം.
ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ മുഴുവൻ പ്രതിനിധിയല്ല: ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി 12 ഏറ്റവും വലിയ ബാങ്കുകളെ ഉൾക്കൊള്ളുന്നുണ്ടെങ്കിലും, ഇന്ത്യയിലെ എല്ലാ ബാങ്കുകളെയും ഇത് പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നില്ല. ചെറിയ ബാങ്കുകൾക്ക് ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റിയുമായി വ്യത്യസ്തമായ ട്രെൻഡുകൾ ഉണ്ടാകാം.
മൊത്തത്തിൽ, ഇന്ത്യൻ ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുടെ ആരോഗ്യവും ദിശാബോധവും മനസ്സിലാക്കാൻ നിക്ഷേപകർക്കും വിപണി പങ്കാളികൾക്കും വേണ്ടിയുള്ള ഒരു മൂല്യവത്തായ ഉപകരണമാണ് ബാങ്ക് നിഫ്റ്റി. ഈ സൂചികയുടെ പ്രകടനം ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുകയും അനുബന്ധമായ അപകടസാധ്യതകളും ഗുണങ്ങളും പരിഗണിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നതിലൂടെ, ബാങ്കിംഗ് മേഖലയുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട കൂടുതൽ വിവരമുള്ള നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ നിങ്ങൾക്ക് എടുക്കാൻ കഴിയും.
FINNIFTY Explained: A Deep Dive into the Indian Financial Sector
Unlike the Nifty 50, which focuses on the top 50 companies across sectors, FINNIFTY specifically targets the financial services sector.
It comprises 20 of the largest and most liquid financial services companies listed on the NSE.
These companies can be broadly categorized into:
Banks (public and private)
Insurance companies (life and non-life)
Housing finance companies
Non-banking financial companies (NBFCs)
Why is FINNIFTY Important?
Provides a Benchmark for Financial Sector Performance: FINNIFTY reflects the overall performance of the financial services sector. An upward trend in the index indicates a positive outlook, while a downward trend suggests a cautious sentiment.
Facilitates Informed Investment Decisions: Investors and fund managers use FINNIFTY to make informed decisions about investing in financial services companies or financial sector-focused mutual funds and ETFs.
Underlying Asset for Derivatives: FINNIFTY serves as the underlying asset for derivative instruments like futures and options contracts. These allow traders to speculate on the future movement of the financial services sector's performance.
Benefits of Tracking FINNIFTY:
Early Warning Signals: Monitoring FINNIFTY can help investors identify potential risks or opportunities in the financial services sector before they become apparent in individual company stocks.
Sectoral Performance Comparison: Investors holding financial services stocks or sector-specific funds can compare their performance to FINNIFTY to assess their relative returns.
Understanding Market Sentiment: FINNIFTY provides insights into the overall market sentiment towards the financial services sector, aiding investors in making informed decisions.
Things to Consider About FINNIFTY:
More Sector-Specific Risk: Since FINNIFTY focuses on a single sector, it can be more volatile than the broader Nifty 50 index, which is diversified across sectors.
Doesn't Represent the Entire Sector: While FINNIFTY includes the 20 largest financial services companies, it doesn't encompass every player in the sector. Smaller companies may not necessarily follow the same trends as the FINNIFTY.
Overall, FINNIFTY is a valuable tool for investors and market participants to understand the health and direction of the Indian financial services sector. By tracking its performance and considering the associated risks and benefits, you can make more informed investment decisions related to financial services companies
ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റി എന്താണ്?
ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റി എന്നത് 'നിഫ്റ്റി ഫിനാൻഷ്യൽ സർവീസസ് ഇൻഡെക്സ്' എന്നതിന്റെ ചുരുക്കപ്പേരാണ്. ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ധനകാര്യ സേവന മേഖലയുടെ പ്രകടനം ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്ന ഒരു ഓഹരി വിപണി സൂചികയാണിത്. 2021 ൽ നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (NSE) ആണ് ഇത് ആരംഭിച്ചത്. ഇന്ത്യൻ സമ്പദ്വ്യവസ്ഥയുടെ ഈ പ്രധാന ഭാഗത്തിന്റെ ആരോഗ്യവും ദിശാബോധവും അളക്കാൻ നിക്ഷേപകർക്കും വിശകലന വിദഗ്ധർക്കും വേണ്ടിയുള്ള ഒരു നിർണായക ബെഞ്ച്മാർക്കാണിത്.
ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റിയിൽ എന്തൊക്കെ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു:
എല്ലാ സെക്ടറുകളിലുമുള്ള ടോപ്പ് 50 കമ്പനികളെ ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്ന നിഫ്റ്റി 50 ൽ നിന്ന് വ്യത്യസ്തമായി, ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റി പ്രത്യേകിച്ച് ധനകാര്യ സേവന മേഖലയിൽ ശ്രദ്ധ കേന്ദ്രീകരിക്കുന്നു.
NSE യിൽ ലിസ്റ്റുചെയ്തിരിക്കുന്ന 20 ഏറ്റവും വലുതും ഏറ്റവും ദ്രവ്യതയുള്ളതുമായ ധനകാര്യ സേവന കമ്പനികളാണ് ഇതിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നത്.
ഈ കമ്പനികളെ വിശാലമായി തരം തിരിക്കാം:
ബാങ്കുകൾ (പൊതുമേഖലയും സ്വകാര്യവും)
ഇൻഷുറൻസ് കമ്പനികൾ (ജീവൻ, അല്ലാത്ത ജീവൻ)
ഹൗസിംഗ് ഫിനാൻസ് കമ്പനികൾ
നോൺ-ബാങ്കിംഗ് ഫിനാൻഷ്യൽ കമ്പനികൾ (NBFC-കൾ)
ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റി പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടത് എന്തുകൊണ്ട്?
ധനകാര്യ സേവന മേഖലയുടെ പ്രകടനത്തിനുള്ള ഒരു ബെഞ്ച്മാർക്ക് നൽകുന്നു: ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റി ധനകാര്യ സേവന മേഖലയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള പ്രകടനം പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. സൂചികയിലെ വർദ്ധനവ് ഈ മേഖലയോടുള്ള പോസിറ്റീവ് വികാരത്തെയും കുറവ് ജാഗ്രതയെയും സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു.
വിവരമുള്ള നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ എളുപ്പമാക്കുന്നു: ധനകാര്യ സേവന കമ്പനികളിലോ ധനകാര്യ സേവന മേഖലാ കേന്ദ്രീകൃത മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകളിലോ ETF-കളിലോ (എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ട്രേഡഡ് ഫണ്ടുകൾ) നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള വിവരമുള്ള തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ എടുക്കാൻ നിക്ഷേപകരും ഫണ്ട് മാനേജർമാരും ഫിൻനിഫ്റ്റി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
NIFTY FARMA
Nifty Pharma Explained: A Look at India's Pharmaceutical Powerhouse
The Nifty Pharma index is a vital benchmark for gauging the health and performance of the pharmaceutical sector in India. It's a valuable tool for investors, analysts, and anyone interested in this crucial industry. Here's a breakdown of Nifty Pharma:
What is Nifty Pharma?
Launched in 2015 by the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India.
Tracks the performance of the 13 largest and most liquid pharmaceutical companies listed on the NSE.
These companies are selected based on factors like market capitalization (total market value) and trading volume.
Why is Nifty Pharma Important?
Represents the Pharmaceutical Industry: Nifty Pharma reflects the overall health of the Indian pharmaceutical sector. A rising index indicates a positive outlook for the industry, while a decline suggests a cautious sentiment.
Helps Make Investment Decisions: Investors considering pharmaceutical stocks or pharma-focused mutual funds and ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) can use Nifty Pharma as a reference point to evaluate performance.
Provides Insights for Businesses: Pharmaceutical companies can track Nifty Pharma to understand industry trends and benchmark their performance against the leading players.
Benefits of Tracking Nifty Pharma:
Early Signs of Industry Trends: Monitoring Nifty Pharma can help identify potential opportunities or challenges in the Indian pharmaceutical sector before they become apparent in individual company stocks.
Performance Comparison: Investors holding pharma stocks or sector-specific funds can compare their returns to Nifty Pharma's performance.
Understanding Market Sentiment: Nifty Pharma offers insights into investor sentiment towards the pharmaceutical industry, aiding informed decision-making.
Things to Consider About Nifty Pharma:
Sector-Specific Volatility: The Nifty Pharma is more volatile than broader indices like Nifty 50 because it focuses on a single sector.
Doesn't Cover Entire Industry: While Nifty Pharma features the 13 largest companies, it doesn't encompass all Indian pharmaceutical firms. Smaller players may not necessarily follow the same trends.
Overall, the Nifty Pharma index is a powerful tool for understanding the Indian pharmaceutical landscape. By tracking its performance and considering the associated factors, you can gain valuable insights for investment decisions and general industry knowledge..
Nifty IT index
Nifty IT: A Window into India's Booming Tech Sector
The Nifty IT index is a crucial indicator for gauging the performance of the information technology (IT) sector in India. It serves as a valuable tool for investors, analysts, and anyone interested in this dynamic and rapidly growing industry.
Understanding Nifty IT:
Launched in 1999 by the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India.
Tracks the performance of the top 10 largest and most liquid IT companies listed on the NSE.
Selection is based on market capitalization (total market value) and trading activity.
Why is Nifty IT Important?
Represents India's IT Powerhouse: Nifty IT reflects the overall health of the Indian IT sector, a major contributor to the country's economy. A rising index indicates a positive outlook for the industry, while a decline suggests a cautious sentiment.
Informs Investment Decisions: Investors considering IT stocks or IT-focused mutual funds and ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) can use Nifty IT as a benchmark to evaluate potential returns.
Tracks Industry Trends: Businesses in the IT sector can track Nifty IT to understand industry trends, identify potential growth areas, and benchmark their performance against leading players.
Benefits of Following Nifty IT:
Early Indication of Trends: Monitoring Nifty IT can help identify potential opportunities or challenges in the Indian IT sector before they become apparent in individual company stocks.
Performance Comparison: Investors holding IT stocks or sector-specific funds can compare their returns to the performance of Nifty IT.
Understanding Market Sentiment: Nifty IT offers insights into investor sentiment towards the IT industry, aiding informed investment decisions.
Things to Consider About Nifty IT:
Sector-Specific Focus: Nifty IT focuses on a single sector, making it more volatile compared to broader indices like Nifty 50.
Limited Representation: While Nifty IT features the top 10 companies, it doesn't encompass all Indian IT firms. Smaller players may not necessarily follow the same trends.
Weightage Caps: The weightage of any single company in Nifty IT is capped at 25%, ensuring broader representation within the top 10 companies.
Overall, the Nifty IT index is a valuable tool for understanding the health and direction of the Indian IT sector. By tracking its performance and considering the associated factors, you can gain valuable insights for investment decisions, industry analysis, and general knowledge of this key sector.
NIFTY MIDCAP INDEX
Unveiling the Nifty Midcap Index: A Look at India's Growth Potential
The Nifty Midcap Index is a significant benchmark that tracks the performance of mid-sized companies in India. It serves as a window into the potential of these companies to become future leaders of the Indian economy. Here's a detailed explanation:
What is the Nifty Midcap Index?
Launched in 2009 by the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India.
Tracks the performance of the 150 largest and most liquid mid-cap companies listed on the NSE.
Selection is based on market capitalization (total market value) and trading activity. These companies typically fall between the Nifty 50 (large-cap) and Nifty Smallcap (small-cap) indices in terms of size.
Why is the Nifty Midcap Index Important?
Represents Growth Potential: Mid-cap companies often have higher growth prospects compared to large-cap companies. The Nifty Midcap Index reflects the overall health and potential of this growth segment.
Investment Opportunities: Investors seeking higher returns with a calculated risk appetite can utilize the Nifty Midcap Index to identify promising mid-cap stocks or explore mid-cap focused mutual funds and ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds).
Understanding Market Breadth: The Nifty Midcap Index, along with Nifty 50 and Smallcap indices, provides a comprehensive view of the overall Indian stock market by covering companies of various sizes.
Benefits of Tracking the Nifty Midcap Index:
Early Identification of Opportunities: Monitoring the Nifty Midcap Index can help investors identify potentially high-growth companies before they become widely recognized.
Performance Benchmark: Investors holding mid-cap stocks or sector-specific funds can benchmark their performance against the Nifty Midcap Index.
Diversification Potential: The Nifty Midcap Index offers diversification benefits within the broader Indian market, potentially reducing overall portfolio risk.
Things to Consider About the Nifty Midcap Index:
Higher Volatility: Compared to large-cap indices like Nifty 50, the Nifty Midcap Index can be more volatile due to the inherent growth stage of the companies it represents.
Limited Liquidity: Mid-cap stocks may have lower trading volumes compared to large-cap stocks, potentially impacting their immediate buying or selling.
Greater Research Required: In-depth research on individual companies is often recommended before investing in mid-cap stocks due to their higher risk-reward profile.
Overall, the Nifty Midcap Index is a valuable tool for investors and analysts seeking to understand the growth potential of the Indian stock market. By tracking its performance and considering the associated risks and benefits, you can make informed investment decisions and gain insights into the future of the Indian economy.
LARGE CAP STOCKS IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET
Large Cap Stocks: The Backbone of the Indian Stock Market
Large-cap stocks are the heavyweights of the Indian stock market. They represent the biggest and most well-established companies in the country, playing a crucial role in the overall market performance. Here's a breakdown of what you need to know:
What are Large-Cap Stocks?
Defined by Market Capitalization: Large-cap stocks are companies with a market capitalization (total market value of outstanding shares) exceeding a specific threshold. This threshold can vary depending on the source, but it generally falls well above ₹20,000 crore (₹200 billion) in India.
Top Players in Their Sectors: Large-cap companies are typically dominant players in their respective industries. They have a proven track record of consistent revenue, profitability, and a strong brand presence.
Examples of Large-Cap Stocks in India (as of March 24, 2024):
Reliance Industries Ltd. (RIL)
Tata Consultancy Services (TCS)
HDFC Bank
Infosys Ltd.
Hindustan Unilever Ltd. (HUL)
Why are Large-Cap Stocks Important?
Stability and Reliability: Large-cap stocks are generally considered less volatile compared to mid-cap and small-cap stocks. Their established track record and financial strength offer a degree of stability for investors seeking lower-risk options.
Liquidity: Large-cap stocks are actively traded on the stock exchanges, making it easier for investors to buy and sell them without significant price impact.
Blue-Chip Status: Large-cap stocks are often referred to as "blue-chip" stocks, signifying their reputation, financial strength, and long-term growth potential.
Benefits of Investing in Large-Cap Stocks:
Reduced Volatility: Compared to smaller companies, large-cap stocks tend to experience smaller price fluctuations, offering a more predictable investment option.
Regular Dividends: Many large-cap companies have a history of paying regular dividends to shareholders, providing a source of passive income.
Portfolio Diversification: Including large-cap stocks in your portfolio can help balance out the risk associated with investing in smaller, more volatile companies.
Things to Consider About Large-Cap Stocks:
Lower Growth Potential: While large-cap stocks offer stability, their growth potential may be lower compared to mid-cap and small-cap stocks.
Higher Investment Cost: Due to their established status, large-cap stocks are generally more expensive than smaller companies.
Limited Upside Potential: The potential for significant price appreciation in large-cap stocks may be limited compared to high-growth smaller companies.
Overall, large-cap stocks are a cornerstone of any well-diversified investment portfolio in the Indian stock market. They offer stability, liquidity, and the potential for steady returns. However, it's important to consider your investment goals and risk tolerance before investing in any stock, including large-cap companies.
Large cap STOCKS എന്താണ് വിശദമാക്കുക
ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ നട്ടായസ്ഥികളാണ്. ഇവ രാജ്യത്തെ ഏറ്റവും വലുതും ഏറ്റവും പ്രതിഷ്ഠ നേടിയതുമായ കമ്പനികളെ പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നു, മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള വിപണി പ്രകടനത്തിൽ നിർണായക പങ്ക് വഹിക്കുന്നു.
എന്താണ് ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ?
വിപണി മൂലധനം വഴി നിർവചിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു: ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത പരിധി കവിയുന്ന വിപണി മൂലധനം (പുറത്തിറങ്ങിയ ഓഹരികളുടെ മൊത്തം വിപണി മൂല്യം) ഉള്ള കമ്പനികളാണ്. ഈ പരിധി ഏത് സ്രോതസ്സിൽ നിന്നാണ് ലഭിക്കുന്നത് എന്നതിനെ ആശ്രയിച്ച് വ്യത്യാസപ്പെടാം, പക്ഷേ ഇന്ത്യയിൽ ഇത് സാധാരണയായി ₹20,000 കോടിയിൽ (₹200 ബില്യൺ) കൂടുതലായിരിക്കും.
അതത് മേഖലകളിലെ മുൻനിര കളിക്കാർ: ലാർജ് കാപ് കമ്പനികൾ സാധാരണയായി അതത് വ്യവസായങ്ങളിൽ മുൻനിര കളിക്കാരാണ്. ഇവയ്ക്ക് സ്ഥിരത തെളിയിക്കപ്പെട്ട വരുമാനം, ലാഭം എന്നിവയുടെയും ശക്തമായ ബ്രാൻഡ് സാന്നിധ്യത്തിന്റെയും ഒരു ചരിത്രമുണ്ട്.
ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകളുടെ ഉദാഹരണങ്ങൾ (2024 മാർച്ച് 24 വരെ):
റिलायൻസ് ഇൻഡസ്ട്രീസ് ലിമിറ്റഡ് (RIL)
ടാറ്റ കൺസൾട്ടൻസി സർവീസസ് (TCS)
എച്ച്ഡിഎഫ്സി ബാങ്ക്
ഇൻഫോസിസ് ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ഹിന്ദുസ്ഥാൻ യൂണിലിവർ ലിമിറ്റഡ് (HUL)
എന്തുകൊണ്ടാണ് ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടത്?
സ്ഥിരതയും വിശ്വാസ്യതയും: മിഡ് കാപ്, സ്മോൾ കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകളെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച് ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ സാധാരണയായി കുറഞ്ഞ വിലാപം അനുഭവപ്പെടുന്നു. കുറഞ്ഞ അപകടസാധ്യതയുള്ള ഓപ്ഷനുകൾ തേടുന്ന നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് അവരുടെ സ്ഥിരത തെളിയിക്കപ്പെട്ട ട്രാക്ക് റെക്കോർഡും ധനകാര്യ ശേഷിയും ഒരു പരിധി വരെ സ്ഥിരത വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നു.
ലിക്വിഡിറ്റി: ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ ഓഹരി വിപണികളിൽ സജീവമായി വ്യാപാരം നടത്തുന്നു, ഇത് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് വിലയിൽ കാര്യമായ മാറ്റം വരുത്താതെ അവ വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനും എളുപ്പമാക്കുന്നു.
ബ്ലൂ-ചിപ്പ് സ്റ്റാറ്റസ്: ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകളെ പലപ്പോഴും "ബ്ലൂ-ചിപ്പ്" സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ എന്ന് വിളിക്കാറുണ്ട്,
MIDCAP STOCKS
Mid-cap stocks occupy the middle ground in the Indian stock market, offering a compelling blend of growth potential and calculated risk for investors. Here's a deep dive into this exciting category:
What are Mid-Cap Stocks?
Defined by Market Capitalization: Mid-cap stocks represent companies with a market capitalization (total market value) typically ranging from ₹5,000 crore (₹50 billion) to ₹20,000 crore (₹200 billion) in India. This range can vary depending on the classification method used.
Bridge Between Large and Small Caps: Mid-cap companies are often seen as a bridge between established large-cap players and emerging small-cap businesses. They are well-defined players in their sectors but have room for significant growth.
Examples of Mid-Cap Stocks in India (as of March 24, 2024):
Bajaj Finance Ltd.
Marico Ltd.
Havells India Ltd.
Macrotech Developers Ltd.
Indian Hotels Company Ltd. (Taj Hotels)
Why are Mid-Cap Stocks Important?
High Growth Potential: Compared to large-cap stocks, mid-cap companies have the potential for significant growth as they expand their market share and reach. This can lead to substantial returns for investors.
Diversification Opportunities: Including mid-cap stocks in your portfolio can help diversify your holdings beyond large-cap companies, potentially reducing overall investment risk.
Future Leaders: Many mid-cap companies have the potential to evolve into future large-cap leaders of the Indian economy. Investing early can allow you to capture this growth potential.
Benefits of Investing in Mid-Cap Stocks:
Higher Return Potential: Mid-cap stocks offer the potential for higher returns compared to large-cap stocks due to their higher growth prospects.
Relatively Lower Volatility: While riskier than large-cap stocks, mid-cap stocks may experience less volatility compared to small-cap stocks.
Access to Emerging Sectors: Mid-cap companies are often present in fast-growing sectors, allowing you to participate in the potential of these industries.
Things to Consider About Mid-Cap Stocks:
Higher Risk: Compared to large-cap stocks, mid-cap stocks are inherently riskier due to their growth stage and potential for fluctuations.
Lower Liquidity: Mid-cap stocks may have lower trading volumes compared to large-cap stocks, impacting the ease of buying or selling them quickly.
Greater Research Required: In-depth research on individual companies is crucial before investing in mid-cap stocks due to the varying risk profiles within this category.
Overall, mid-cap stocks offer an attractive proposition for investors seeking a balance between growth potential and calculated risk. By understanding their characteristics and associated considerations, you can make informed investment decisions and potentially benefit from the exciting growth stories within the Indian mid-cap segment.
MID cap എന്താണ് വിശദമാക്കുക
മിഡ് കാപ് വിപണി വിഭാഗം ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് വളർച്ചയും അപകടസാധ്യതയും തമ്മിലുള്ള ഒരു സന്തുലിതാവസ്ഥ നൽകുന്നു. ഈ ആവേശകരമായ വിഭാഗത്തെക്കുറിച്ച് കൂടുതൽ അറിയാം:
എന്താണ് മിഡ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ?
വിപണി മൂലധനം വഴി നിർവചിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു: മിഡ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ സാധാരണയായി ₹5,000 കോടി (₹50 ബില്യൺ) മുതൽ ₹20,000 കോടി (₹200 ബില്യൺ) വരെയുള്ള വിപണി മൂലധനം (പുറത്തിറങ്ങിയ っておりる [oriru - issued] ഓഹരികളുടെ മൊത്തം വിപണി മൂല്യം) ഉള്ള കമ്പനികളെയാണ് പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നത്. ഈ പരിധി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന വർगीകരണ രീതിയെ ആശ്രയിച്ച് വ്യത്യാസപ്പെടാം.
ലാർജ് കാപ്പിനും സ്മോൾ കാപ്പിനും ഇടയിലുള്ള പാലം: സ്ഥാപിതമായ ലാർജ് കാപ് കളിക്കാരും ഉയർന്നുവരുന്ന സ്മോൾ കാപ് ബിസിനസുകളും തമ്മിലുള്ള ഒരു പാലമായിട്ടാണ് മിഡ് കാപ് കമ്പനികളെ പലപ്പോഴും കാണുന്നത്. അവ അതത് മേഖലകളിൽ വ്യക്തമായി നിർവചിക്കപ്പെട്ട കളിക്കാരാണ്, പക്ഷേ കാര്യമായ വളർച്ചയ്ക്കുള്ള സാധ്യതയുമുണ്ട്.
ഇന്ത്യയിലെ മിഡ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകളുടെ ഉദാഹരണങ്ങൾ (2024 മാർച്ച് 24 വരെ):
ബജാജ് ഫിനാൻസ് ലിമിറ്റഡ്
മാരിക്കോ ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ഹവells ഇന്ത്യ ലിമിറ്റഡ്
മैकറോടെക് ഡവലപ്പേഴ്സ് ലിമിറ്റഡ്
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഹോട്ടൽസ് കമ്പനി ലിമിറ്റഡ് (താജ് ഹോട്ടലുകൾ)
എന്തുകൊണ്ടാണ് മിഡ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടത്?
ഉയർന്ന വളർച്ചയുടെ സാധ്യത: ലാർജ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകളെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച്, മിഡ് കാപ് കമ്പനികൾക്ക് വിപണി വിഹിതം വർധിപ്പിക്കുകയും എത്തുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നതോടൊപ്പം കാര്യമായ വളർച്ചയ്ക്കുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്. ഇത് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് കാര്യമായ നേട്ടങ്ങൾ നൽകിയേക്കാം.
വൈവിധ്യവത്കരണ അവസരങ്ങൾ: നിങ്ങളുടെ പോർട്ട്ഫോリオയിൽ മിഡ് കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ ഉൾപ്പെടുത്തുന്നത് ലാർജ് കാപ് കമ്പനികൾക്കപ്പുറം നിങ്ങളുടെ ഹോൾഡിംഗുകൾ വൈവിധ്യവത്കരിക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കും, ഇത് മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള നിക്ഷേപ അപകടസാധ്യത കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു.
ഭാവി നേതാക്കൾ: ധാരാളം മിഡ് കാപ് കമ്പനികൾക്കും ഭാവിയിൽ ഇന്ത്യൻ സമ്പദ്വ്യവസ്ഥയുടെ ലാർജ് കാപ് നേതാക്കളായി മാറാനുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്.
SMALL CAP STOCKS
Small-cap stocks represent the younger, emerging companies within the Indian stock market. They offer an exciting opportunity for investors seeking high growth potential, but also come with inherent risks. Here's a breakdown of what you need to understand:
What are Small-Cap Stocks?
Defined by Market Capitalization: Small-cap stocks are companies with a market capitalization (total market value of outstanding shares) typically below ₹5,000 crore (₹50 billion) in India. This range can vary depending on the classification method used.
Emerging Players: Small-cap companies are often in the early stages of growth, aiming to establish themselves in their respective markets. They may have innovative ideas or disruptive business models.
Examples of Small-Cap Stocks in India (as of March 24, 2024):
New-age technology startups
Biotech companies developing new drugs
Upcoming players in the renewable energy sector
Why are Small-Cap Stocks Important?
High Growth Potential: Small-cap companies have the potential for explosive growth as they expand their market reach and establish their products or services. This can lead to significant returns for investors who enter early.
High-Risk, High-Reward Potential: The potential for high returns in small-cap stocks is balanced by the risk of high volatility and even potential failure. Careful research and risk management are crucial.
Access to Innovative Sectors: Small-cap companies are often at the forefront of innovation, allowing investors to participate in the potential of emerging industries.
Benefits of Investing in Small-Cap Stocks:
Potentially Higher Returns: Compared to established large-cap companies, small-cap stocks offer the possibility of much higher returns due to their high growth prospects.
Exposure to New Ideas: Investing in small-cap stocks can give you exposure to innovative ideas and disruptive technologies that could shape the future.
Greater Diversification: Including small-cap stocks in your portfolio can help diversify your holdings beyond established companies, potentially reducing overall risk.
Things to Consider About Small-Cap Stocks:
High Volatility: Small-cap stocks are generally more volatile than large-cap stocks, meaning their prices can fluctuate significantly in a short period.
Lower Liquidity: Small-cap stocks may have lower trading volumes compared to larger companies, making it potentially difficult to buy or sell them quickly at your desired price.
Limited Track Record: Due to their early stage, small-cap companies may have a shorter track record, making it challenging to assess their future performance.
Overall, small-cap stocks are a fascinating but risky proposition for investors. They offer the potential for high growth and participation in exciting new ventures. However, careful research, risk management, and a long-term investment horizon are essential before venturing into this dynamic segment of the Indian stock market.
SMALL cap STOCKS എന്താണ് വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിലെ ചെറുതും എന്നാൽ വളർന്നുവരുന്നതുമായ കമ്പനികളെയാണ് സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ പ്രതിനിധീകരിക്കുന്നത്. നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഉയർന്ന വളർച്ചയുടെ സാധ്യത വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്ന ഇവ, അതേസമയം അന്ത inherent [inherent - inherent] അപകടസാധ്യതകളും ഒപ്പം വരുന്നു. ഇവയെക്കുറിച്ച് കൂടുതൽ മനസിലാക്കേണ്ട കാര്യങ്ങൾ ഇതാ:
എന്താണ് സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ?
വിപണി മൂലധനം വഴി നിർവചിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു: സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ സാധാരണയായി ₹5,000 കോടി (₹50 ബില്യൺ) ത്തിൽ താഴെ വിപണി മൂലധനം (പുറത്തിറങ്ങിയ ഓഹരികളുടെ മൊത്തം വിപണി മൂല്യം) ഉള്ള കമ്പനികളാണ്. ഇന്ത്യയിൽ ഈ പരിധി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്ന വർगीകരണ രീതിയെ ആശ്രയിച്ച് വ്യത്യാസപ്പെടാം.
ഉയർന്നുവരുന്ന കളിക്കാർ: സ്മॉल കാപ് കമ്പനികൾ പലപ്പോഴും വളർച്ചയുടെ ആദ്യ ഘട്ടത്തിലാണ്, അതത് വിപണികളിൽ സ്വന്തം കാൽപ്പാട് ഉറപ്പിക്കാൻ ലക്ഷ്യമിടുന്നു. ഇവയ്ക്ക് വിപ്ലവകരമായ ബിസിനസ് മോഡലുകളോ പുതിയ ആശയങ്ങളോ ഉണ്ടായേക്കാം.
ഇന്ത്യയിലെ സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾക്കുള്ള ഉദാഹരണങ്ങൾ (2024 മാർച്ച് 24 വരെ):
പുതിയ തലമുറ ടെക്നോളജി സ്റ്റാർട്ടപ്പുകൾ
പുതിയ മരുന്നുകൾ വികസിപ്പിക്കുന്ന ബയോടെക് കമ്പനികൾ
പുനരുപयोग ഊർജ്ജ क्षेत्र [kshetra - sector] ത്തിലെ ഉയർന്നുവരുന്ന കളിക്കാർ
എന്തുകൊണ്ടാണ് സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകൾ പ്രധാനപ്പെട്ടത്?
ഉയർന്ന വളർച്ചയുടെ സാധ്യത: വിപണിയിൽ എത്തുകയും ഉൽപ്പന്നങ്ങളോ സേവനങ്ങളോ സ്ഥാപിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നതോടെ സ്മॉल കാപ് കമ്പനികൾക്ക് സ്ഫോടനാത്മകമായ വളർച്ചയ്ക്കുള്ള സാധ്യതയുണ്ട്. ഇത് നേരത്തെ പ്രവേശിക്കുന്ന നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് കാര്യമായ നേട്ടങ്ങൾ നൽകിയേക്കാം.
ഉയർന്ന അപകടസാധ്യത, ഉയർന്ന നേട്ട സാധ്യത: ഉയർന്ന വളർച്ചയുടെ സാധ്യതകൾ സ്മॉल കാപ് സ്റ്റോക്കുകളിൽ ഉണ്ടെങ്കിലും, അതേസമയം ഉയർന്ന വിലാപവും പരാജയ സാധ്യതയും ഇവയ്ക്കുണ്ട്. ശ്രദ്ധാപൂർവ്വമായ ഗവേഷണവും അപകടസാധ്യത നിരീക്ഷണവും [risk management] അത്യാവശ്യമാണ്.
ETF FUNDS?
Demystifying ETFs: A Blend of Stocks and Mutual Funds in the Indian Market
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) are innovative investment vehicles that offer a compelling combination of features from both stocks and mutual funds. Here's a breakdown to understand how they work and their potential benefits for Indian investors:
What is an ETF?
An ETF tracks a basket of underlying assets, which can be stocks, bonds, commodities, or even a mix of these.
It trades on a stock exchange just like individual stocks, meaning you can buy or sell units (shares) of the ETF throughout the trading day.
How are ETFs Different from Mutual Funds?
Trading Mechanism: Unlike mutual funds, which are typically priced and bought/sold once a day at the end of the trading session, ETFs trade continuously throughout the day like stocks. This allows for more flexibility and potentially faster execution of trades.
Management: ETFs are passively managed, meaning they aim to replicate the performance of the underlying index they track. Mutual funds, on the other hand, can be actively managed, where fund managers try to outperform the market.
Benefits of Investing in ETFs:
Diversification: ETFs provide instant diversification with a single investment, as they hold a basket of assets. This can help spread your risk and reduce the impact of volatility in any single holding.
Low Cost: Compared to actively managed mutual funds, ETFs generally have lower expense ratios, making them a more cost-effective way to invest.
Transparency: Holdings of an ETF are typically disclosed daily, offering investors greater transparency into the underlying assets.
Tax Efficiency: ETFs can be tax-efficient due to their structure and low trading activity within the fund itself. However, consult a tax advisor for specific details.
Flexibility: You can buy and sell ETF units on the stock exchange throughout the day, offering greater flexibility compared to mutual funds.
Types of ETFs in India:
Equity ETFs: Track a specific stock market index, such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex.
Debt ETFs: Invest in government bonds or corporate bonds.
Commodity ETFs: Track the price of commodities like gold, silver, or oil.
Gold ETFs: A popular option in India, these ETFs invest primarily in physical gold.
Are ETFs Right for You?
ETFs can be a valuable tool for investors seeking diversification, low costs, and transparency. However, it's essential to consider your investment goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before choosing any ETF.
Remember: Conduct thorough research on the specific ETF you're considering, including its underlying holdings, expense ratio, and tracking performance. Consulting a financial advisor can be helpful for making informed investment decisions.
MAJOR ETF FUNDS
India's Major Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs): An Outline
Overview: ETFs are a popular investment option in India, offering a blend of features from stocks and mutual funds. They track a basket of underlying assets and trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks.
Major ETF Categories:
Equity ETFs: These track stock market indices.
Nifty 50 ETFs: Track the Nifty 50 index, representing the 50 largest and most liquid companies in India. (e.g., Nippon India ETF Nifty 50 Bees, ICICI Nifty 50 ETF)
Sectoral ETFs: Focus on specific sectors like banking, infrastructure, or IT. (e.g., Banking ETFs, Infrastructure ETFs, Information Technology ETFs)
Gold ETFs: Invest primarily in physical gold, reflecting gold price fluctuations. (e.g., Reliance Gold Savings Fund, SBI Gold ETF)
Debt ETFs: Invest in government or corporate bonds, offering exposure to the debt market.
Short Term Debt ETFs: Invest in short-term bonds with lower volatility. (e.g., Nippon India Liquid ETF, Invesco Liquid Debt ETF)
Corporate Bond ETFs: Invest in corporate bonds, offering potentially higher returns but with credit risk. (e.g., ICICI Corporate Bond ETF, SBI Corporate Bond ETF)
Benefits of Investing in ETFs:
Diversification: Gain exposure to a basket of assets in a single investment, reducing risk.
Low Cost: Generally lower expense ratios compared to actively managed mutual funds.
Transparency: Holdings are typically disclosed daily for better understanding.
Liquidity: Can be easily bought and sold throughout the trading day.
Flexibility: Offer greater flexibility compared to mutual funds with single-day pricing.
Important Considerations:
Investment Goals: Align your ETF selection with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
Underlying Holdings: Research the specific assets the ETF holds before investing.
Expense Ratio: Consider the ongoing fees associated with the ETF.
Disclaimer: This is a general outline. Conduct thorough research on specific ETFs before investing.
NIFTY BEES
Nifty Bees, formally known as Nippon India ETF Nifty 50 Bees, is a popular Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) traded on Indian stock exchanges, primarily the National Stock Exchange (NSE). It functions by mirroring the performance of the Nifty 50 index, a benchmark index that tracks the 50 largest and most liquid companies listed on the NSE.
Here's a closer look at what Nifty Bees offers:
Exposure to Top Indian Companies: By investing in Nifty Bees, you gain exposure to the performance of the leading 50 Indian companies in a single investment. This provides instant diversification and reflects the overall health of the Indian stock market.
Cost-Effective Option: Compared to directly investing in all 50 Nifty 50 companies, Nifty Bees offers a more affordable way to participate in the Indian market. ETFs generally come with lower expense ratios compared to actively managed mutual funds.
Trading Flexibility: Unlike mutual funds with a single daily price, Nifty Bees function like stocks, trading throughout the exchange's trading session. This allows for greater flexibility in buying and selling units (shares) at the current market price.
In essence, Nifty Bees act as a convenient and cost-effective way for investors to gain exposure to the large-cap segment of the Indian stock market.
Some additional key points about Nifty Bees:
Type of Investment: It's an Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) that tracks an underlying index, in this case, the Nifty 50.
Management Style: Nifty Bees are passively managed. This means they aim to replicate the Nifty 50 index's performance by holding the same stocks in proportion to their weightage within the index.
Liquidity: Due to its popularity and tracking a major market index, Nifty Bees boast high liquidity. This translates to easy buying and selling of units on the stock exchange.
Things to Consider Before Investing in Nifty Bees:
Investment Goals & Risk Tolerance: Ensure your investment goals and risk tolerance align with this type of investment.
Research: Research the Nifty 50 index and the companies it comprises to understand the underlying holdings.
Fees: Consider the expense ratio and other associated fees of Nifty Bees.
In conclusion, Nifty Bees are a valuable tool for investors seeking diversification and exposure to leading Indian companies through a single investment.
NIFTY BEES എന്താണ് എന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
നിഫ्टी ബീസ് (ഔദ്യോഗിക നാമം: നിപ്പോൺ ഇന്ത്യ ETF നിഫ्टी 50 ബീസ്) ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണികളിൽ, പ്രധാനമായും നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചിൽ (NSE) വ്യാപാരം ചെയ്യുന്ന ഒരു പ്രചാരമേറിയ എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ട്രേഡेड ഫണ്ട് (ETF) ആണ്. നിഫ्टी 50 സൂചികയുടെ പ്രകടനം അനുകരിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെയാണ് ഇത് പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നത്. നിഫ्टी 50 എന്നത് NSE യിൽ ലിസ്റ്റുചെയ്തിരിക്കുന്ന 50 ഏറ്റവും വലുതയുള്ളതും ഏറ്റവും കൂടുതൽ വിനിമയം നടക്കുന്നതുമായ കമ്പനികളുടെ പ്രതിനിധീകരണമാണ്.
നിഫ्टी ബീസ് നിങ്ങൾക്ക് നൽകുന്ന കാര്യങ്ങൾ ഇതാ:
പ്രമുഖ ഇന്ത്യൻ കമ്പനികളിലേക്കുള്ള എക്സ്പോഷർ (Exposure to Top Indian Companies): നിഫ्टी ബീസിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ, ഒറ്റത്തവണ നിക്ഷേപത്തിലൂടെ തന്നെ 50 മുൻനിര ഇന്ത്യൻ കമ്പനികളുടെ പ്രകടനത്തിലേക്ക് നിങ്ങൾക്ക് എക്സ്പോഷർ ലഭിക്കുന്നു. ഇത് ഉടനടി വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം നൽകുകയും ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള പ്രവണതയെ പ്രതിഫലിപ്പിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
ചെലവ് കുറഞ്ഞ ഓപ്ഷൻ (Cost-Effective Option): 50 നിഫ्टी 50 കമ്പനികളിലെല്ലാം നേരിട്ട് നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച്, ഇന്ത്യൻ വിപണിയിൽ പങ്കെടുക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള കൂടുതൽ താങ്ങാനാവുന്ന മാർഗമാണ് നിഫ्टी ബീസ് വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നത്. സാധാരണയായി, ആക്ടീവ് ഫണ്ടുകളെ (Actively Managed Funds) അപേക്ഷിച്ച് ETF-കൾക്ക് കുറഞ്ഞ ചെലവ് അനുപാതം (Expense Ratio) ഉണ്ടായിരിക്കും.
ട്രേഡിംഗ് ലचीലത (Trading Flexibility): ദിവസത്തിൽ ഒരിക്കൽ വില നിശ്ചയിക്കപ്പെടുന്ന മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകളിൽ നിന്ന് വ്യത്യസ്തമായി, ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ വ്യാപാര സെഷൻ മുഴുവനയും ഓഹരികൾ പോലെയാണ് നിഫ्टी ബീസ് വ്യാപാരം ചെയ്യുന്നത്. ഇത് നിലവിലെ വിപണി വിലയിൽ യൂണിറ്റുകൾ (ഷെയറുകൾ) വാങ്ങാനും വിൽക്കാനും കൂടുതൽ ലचीലത നൽകുന്നു.
അടിസ്ഥാനപരമായി, ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിലെ ലാർജ് കാപ് (Large Cap) വിഭാഗത്തിലേക്ക് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് എക്സ്പോഷർ നേടാനുള്ള സൗകര്യപ്രദവും ചെലവ് കുറഞ്ഞതുമായ മാർഗമാണ് നിഫ्टी ബീസ്.
നിഫ्टी ബീസിനെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള കൂടുതൽ ചില പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
നിക്ഷേപ തരം (Type of Investment): നിഫ्टी 50 പോലുള്ള അടിസ്ഥാന സൂചിക ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്ന ഒരു എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ട്രേഡेड ഫണ്ട് (ETF) ആണിത്.
മാനേജ്മെന്റ് രീതി (Management Style): നിഫ्टी ബീസ് നിഷ്ക്രിയമായി നിയന്ത്രിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു (Passively
BANK BEES
The term "Bank Bees" isn't actually a specific Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) traded on the Indian stock market. There isn't a popular ETF with that exact name.
However, it's likely you might be interested in ETFs that focus on the banking sector in India. These are called Banking Sector ETFs.
These ETFs function by tracking a basket of stocks from leading Indian banks. Essentially, by investing in a Banking Sector ETF, you gain exposure to the performance of multiple banks in a single investment.
Here are some benefits of investing in Banking Sector ETFs:
Diversification: Spreads your investment across various banks, reducing risk compared to holding individual bank stocks.
Cost-Effectiveness: Generally, Banking Sector ETFs come with lower expense ratios compared to actively managed mutual funds.
Potential for Growth: If the Indian banking sector performs well, Banking Sector ETFs can offer good returns.
Before considering Banking Sector ETFs, here are some things to keep in mind:
Investment Goals: Ensure your investment goals and risk tolerance align with these ETFs.
Underlying Holdings: Research the specific banks the ETF invests in to understand the composition.
Expense Ratio: Consider the ongoing fees associated with the ETF.
Here are some popular Banking Sector ETFs in India:
SBI Banking ETF
Kotak Banking ETF
Nippon India Banking ETF
ICICI Prudential Banking ETF
HDFC Banking ETF
It's always recommended to carefully review the prospectus of each ETF before making any investment decisions.
BANK BEES എന്താണ് എന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
ബാങ്ക് ബീസ് എന്താണ്?
ബാങ്ക് ബീസ് എന്നത് ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ ലഭ്യമായ ഒരു പ്രധാന എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ട്രേഡഡ് ഫണ്ട് (ETF) അല്ല.
എന്നിരുന്നാലും, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് താൽപ്പര്യമുള്ളത് ബാങ്കിംഗ് സെക്ടർ ETF-കളിൽ ആകാം. ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ നിരവധി ബാങ്കിംഗ് സെക്ടർ ETF-കൾ ലഭ്യമാണ്, അവ ഇന്ത്യയിലെ പ്രധാന ബാങ്കുകളുടെ ഓഹരികളുടെ ഒരു ക篮子 ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്നു.
ബാങ്കിംഗ് സെക്ടർ ETF-കളിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ലഭിക്കുന്ന ചില നേട്ടങ്ങൾ ഇതാ:
വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം: നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപം ഒന്നിലധികം ബാങ്കുകളിലേക്ക് വ്യാപിപ്പിക്കാൻ ഇത് നിങ്ങളെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു, അത് നിങ്ങളുടെ അപകടസാധ്യത കുറയ്ക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കും.
കുറഞ്ഞ ചെലവ്: സാധാരണയായി, സജീവമായി നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്ന മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകളെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച് ETF-കൾക്ക് കുറഞ്ഞ ചെലവ് അനുപാതം ഉണ്ട്.
ലാഭം: ബാങ്കിംഗ് സെക്ടർ നന്നായി പ്രവർത്തിക്കുമ്പോൾ, ഈ ETF-കൾക്ക് നല്ല നേട്ടം നൽകാൻ കഴിയും.
ബാങ്കിംഗ് സെക്ടർ ETF-കളിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് പരിഗണിക്കേണ്ട ചില കാര്യങ്ങൾ ഇതാ:
നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ: നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങളും അപകടസാധ്യത സഹിഷ്ണുതയും ഈ ETF-കളുമായി പൊരുത്തപ്പെടുന്നുണ്ടോ എന്ന് ഉറപ്പാക്കുക.
അടിസ്ഥാന ഹോൾഡിംഗുകൾ: ETF ട്രാക്ക് ചെയ്യുന്ന ഓഹരികളെക്കുറിച്ച് ഗവേഷണം നടത്തുക.
ചെലവ് അനുപാതം: ETF-മായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട തുടർച്ചയായ ഫീസ് പരിഗണിക്കുക.
ഇന്ത്യയിലെ ചില പ്രധാന ബാങ്കിംഗ് സെക്ടർ ETF-കൾ ഇതാ:
SBI Banking ETF
Kotak Banking ETF
Nippon India Banking ETF
ICICI Prudential Banking ETF
HDFC Banking ETF
നിക്ഷേപം നടത്തുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് ഓരോ ETF-യുടെയും പ്രോസ്പെക്ടസ് ശ്രദ്ധാപൂർവ്വം വായിക്കാൻ നിർദ്ദേശിക്കുന്നു.
GOLD BEES
Gold Bees refers to a specific type of Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) traded on the Indian stock market. There are several Gold ETFs available, but a popular one is the Nippon India ETF Gold Bees.
How do Gold Bees Work?
Gold Bees are a type of commodity ETF, meaning they primarily invest in physical gold bullion.
The value of each Gold Bees unit fluctuates based on the international gold price.
When you buy a Gold Bees unit, you're essentially buying a small portion of the physical gold held by the ETF.
Benefits of Investing in Gold Bees:
Hedge Against Inflation: Gold is often seen as a hedge against inflation, as its value tends to rise when the purchasing power of currency falls.
Portfolio Diversification: Gold can add diversification to your portfolio, potentially reducing overall risk.
Liquidity: Gold Bees are highly liquid, meaning you can easily buy and sell units on the stock exchange throughout the trading day.
Convenience: Investing in Gold Bees offers a convenient way to gain exposure to gold without the hassle of physically storing it.
Things to Consider Before Investing in Gold Bees:
Investment Goals: Align your investment goals and risk tolerance with this type of investment. Gold prices can be volatile.
Expense Ratio: Consider the ongoing fees associated with the ETF, including the expense ratio.
Indirect Ownership: While you own units of the ETF, you don't directly own the underlying physical gold.
Here are some additional points about Gold Bees:
They are passively managed, meaning they aim to replicate the performance of the gold price.
They offer greater flexibility compared to physical gold as you can buy and sell them throughout the trading day.
Overall, Gold Bees can be a valuable tool for investors seeking exposure to gold for portfolio diversification or as a hedge against inflation.
GOLDBEESഎന്താണ് എന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
GOLDBEES എന്നത് ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ ലഭ്യമായ ഒരു പ്രധാന എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ട്രേഡഡ് ഫണ്ട് (ETF) ആണ്.
GOLDBEES എങ്ങനെയാണ് പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നത്?
GOLDBEES ഒരു 'കൊമോഡിറ്റി ETF' ആണ്, അതായത് ഇത് പ്രധാനമായും ഭൗതിക സ്വർണ്ണ ബുള്ളിയനിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നു.
ഓരോ GOLDBEES യൂണിറ്റിന്റെയും മൂല്യം അന്താരാഷ്ട്ര സ്വർണ്ണ വിലയെ ആശ്രയിച്ച് ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകൾക്ക് വിധേയമാണ്.
നിങ്ങൾ ഒരു GOLDBEES യൂണിറ്റ് വാങ്ങുമ്പോൾ, നിങ്ങൾ യഥാർത്ഥത്തിൽ ETF സൂക്ഷിച്ചിരിക്കുന്ന ഭൗതിക സ്വർണ്ണത്തിന്റെ ഒരു ചെറിയ ഭാഗം വാങ്ങുകയാണ്.
GOLDBEES-ൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ നേട്ടങ്ങൾ:
പണപ്പെരുപ്പത്തിനെതിരായ പ്രതിരോധം: പണത്തിന്റെ വാങ്ങൽ ശേഷി കുറയുമ്പോൾ സ്വർണ്ണത്തിന്റെ മൂല്യം സാധാരണയായി ഉയരുന്നതിനാൽ ഇത് പണപ്പെരുപ്പത്തിനെതിരായ ഒരു പ്രതിരോധമായി കണക്കാക്കപ്പെടുന്നു.
പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം: സ്വർണ്ണം നിങ്ങളുടെ പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോയിൽ വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം നൽകുകയും മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള അപകടസാധ്യത കുറയ്ക്കുകയും ചെയ്യും.
ലിക്വിഡിറ്റി: GOLDBEES വളരെ ലിക്വിഡ് ആണ്, അതായത് നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ട്രേഡിംഗ് ദിവസം മുഴുവൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചിൽ യൂണിറ്റുകൾ എളുപ്പത്തിൽ വാങ്ങുകയും വിൽക്കുകയും ചെയ്യാം.
സൗകര്യം: ഭൗതിക സ്വർണ്ണം സൂക്ഷിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ബുദ്ധിമുട്ട് ഒഴിവാക്കി സ്വർണ്ണത്തിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കാൻ GOLDBEES ഒരു സൗകര്യപ്രദമായ മാർഗം നൽകുന്നു.
GOLDBEES-ൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് പരിഗണിക്കേണ്ട കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ: ഈ തരത്തിലുള്ള നിക്ഷേപവുമായി നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങളും അപകടസാധ്യത സഹിഷ്ണുതയും പൊരുത്തപ്പെടുന്നുണ്ടോ എന്ന് ഉറപ്പാക്കുക. സ്വർണ്ണ വില വളരെ ചാഞ്ചാട്ടമുള്ളതാണ്.
ചെലവ് അനുപാതം: ETF-മായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട തുടർച്ചയായ ഫീസ്, ചെലവ് അനുപാതം ഉൾപ്പെടെ പരിഗണിക്കുക.
അപ്രത്യക്ഷ ഉടമസ്ഥാവകാശം: നിങ്ങൾ ETF യൂണിറ്റുകൾ സ്വന്തമാക്കുമ്പോൾ, നിങ്ങൾ യഥാർത്ഥത്തിൽ അടിസ്ഥാന ഭൗതിക സ്വർണ്ണം സ്വന്തമാക്കുന്നില്ല.
GOLDBEES-നെക്കുറിച്ചുള്ള ചില അധിക വിവരങ്ങൾ:
അവ നിഷ്ക്രിയമായി നിയന്ത്രിക്കപ്പെടുന്നു, അതായത് അവ സ്വർണ്ണ വിലയുടെ പ്രകടനം അനുകരിക്കാൻ ശ്രമിക്കുന്നു.
IPO എന്താണെന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
In the Indian stock market, an IPO, or Initial Public Offering, is the process where a private company goes public by selling its shares to the public for the first time. This essentially means the company is raising capital by issuing new shares that can be traded on stock exchanges.
Here's a breakdown of what an IPO entails in India:
Company goes public: A private company transitions into a public company, allowing public investors to own a stake in the company.
Capital raising: The main purpose of an IPO is for the company to raise funds by selling new shares. This capital can be used for expansion, debt repayment, or other business activities.
Public trading: After the IPO, the company's shares are listed on stock exchanges like the National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), enabling them to be freely bought and sold by investors.
Overall, an IPO is a significant event for both the company and the Indian stock market. It provides a growth opportunity for the company and a chance for investors to participate in the company's success.
IPO എന്താണ്?
ഒരു സ്വകാര്യ കമ്പനി ആദ്യമായി പൊതുജനങ്ങൾക്ക് ഓഹരികൾ വിൽക്കുന്ന പ്രക്രിയയാണ് IPO അഥവാ Initial Public Offering. ഇതോടെ, കമ്പനി ഒരു പൊതു കമ്പനിയായി മാറുകയും ഓഹരികൾ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകളിൽ വ്യാപാരം ചെയ്യാൻ ലഭ്യമാകുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
IPO യിൽ സംഭവിക്കുന്ന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
ഓഹരി വിൽപ്പന: കമ്പനി പുതിയ ഓഹരികൾ സൃഷ്ടിക്കുകയും അവ പൊതുജനങ്ങൾക്ക് വിൽക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
മൂലധനം സമാഹരിക്കൽ: ഓഹരി വിൽപ്പനയിലൂടെ ലഭിക്കുന്ന പണം കമ്പനിക്ക് വളർച്ച, കടം വീട്ടൽ, പുതിയ സംരംഭങ്ങൾ തുടങ്ങിയ കാര്യങ്ങൾക്കായി ഉപയോഗിക്കാം.
പൊതുവായ ഉടമസ്ഥത: ഓഹരി വാങ്ങുന്ന വ്യക്തികൾ കമ്പനിയുടെ ഓഹരി ഉടമകളായി മാറുകയും കമ്പനിയുടെ ലാഭത്തിൽ പങ്കാളികളാകുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
ഓഹരി വിപണി ലിസ്റ്റിംഗ്: IPO ക്ക് ശേഷം, കമ്പനിയുടെ ഓഹരികൾ നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (NSE) , ബോംബെ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (BSE) തുടങ്ങിയ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകളിൽ ലിസ്റ്റ് ചെയ്യപ്പെടുന്നു.
IPO യുടെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
മൂലധനം സമാഹരിക്കൽ: കമ്പനിക്ക് വളർച്ചയ്ക്കും വിപുലീകരണത്തിനും ധനസഹായം ലഭിക്കുന്നു.
പൊതുജന പങ്കാളിത്തം: കമ്പനിക്ക് പുതിയ ഉപഭോക്താക്കളെയും നിക്ഷേപകരെയും ആകർഷിക്കാൻ സാധിക്കുന്നു.
ബ്രാൻഡ് മൂല്യം വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കൽ: IPO കമ്പനിയുടെ പ്രശസ്തിയും ദൃശ്യപരതയും വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
ഓഹരി ഉടമകൾക്ക് ലാഭം: ഓഹരി വില ഉയരുകയാണെങ്കിൽ ഓഹരി ഉടമകൾക്ക് ലാഭം നേടാൻ സാധിക്കും.
IPO യുടെ ദോഷങ്ങൾ:
നിയന്ത്രണം നഷ്ടപ്പെടൽ: സ്ഥാപകർക്ക് കമ്പനിയുടെ നിയന്ത്രണം ഭാഗികമായി നഷ്ടപ്പെടാം.
ചെലവ്: IPO പ്രക്രിയക്ക് ധാരാളം ചെലവ് വരും.
ഓഹരി വിലയിലെ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകൾ: ഓഹരി വിലയിൽ ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലുകൾ ഉണ്ടാകാം, ഇത് നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് നഷ്ടം വരുത്താം.
IPO യിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ്:
കമ്പനിയുടെ സാമ്പത്തിക പ്രകടനം വിശകലനം ചെയ്യുക.
ഭാവി വളർച്ചാ സാധ്യത വിലയിരുത്തുക.
ഓഹരി വിലയുടെ ന്യായമായ വില നിർണ്ണയിക്കുക.
നിക്ഷേപ അപകടസാധ്യതകൾ മനസ്സിലാക്കുക
DEBUNTURE IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET
In the Indian stock market, debentures are a type of debt instrument similar to bonds, but with a key difference: security.
Here's a breakdown of debentures in the Indian context:
Debentures vs. Bonds:
Security: Bonds are typically secured by collateral, meaning the issuer pledges specific assets to repay the debt in case of default. Debentures, on the other hand, are unsecured. This means that if the company issuing the debenture defaults, there's no guarantee you'll get your money back.
Risk and Return: Due to the lack of security, debentures generally offer higher interest rates compared to bonds with similar credit ratings. This compensates investors for the additional risk they take on.
Types of Debentures:
Redeemable Debentures: These debentures have a maturity date, and the issuer is obligated to repay the principal amount on that date.
Irredeemable Debentures: These debentures do not have a fixed maturity date. The issuer can choose to repay them after a certain period, but they are not obligated to do so.
Convertible Debentures: These debentures can be converted into equity shares of the issuing company at a predetermined price and ratio.
Investing in Debentures:
Higher Risk: Debentures carry a higher risk of default compared to secured bonds. Investors need to carefully evaluate the creditworthiness of the issuing company before investing.
Suitable for: Debentures can be suitable for investors seeking higher potential returns than bonds and willing to accept the additional risk. They can also be attractive to companies with limited collateral to offer for secured debt.
Regulation:
The issuance of debentures in India is regulated by the Companies Act, 2013. This act specifies various requirements for companies issuing debentures, such as credit rating, filing of prospectuses, and creation of Debenture Redemption Reserves.
Overall, debentures can be a valuable tool for companies to raise capital, but investors need to be aware of the higher risks involved compared to bonds. It's crucial to thoroughly research the issuing company's financial health and risk tolerance before investing in debentures.
DEBUNTURE എന്താണെന്ന് വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിൽ, ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ ബോണ്ടുകൾക്ക് സമാനമായ ഒരു തരം കടപ്പത്രമാണ്. എന്നാൽ ഒരു പ്രധാന വ്യത്യാസമുണ്ട്: സുരക്ഷ.
ഡെബഞ്ചറും ബോണ്ടും തമ്മിലുള്ള വ്യത്യാസം:
സുരക്ഷ: ബോണ്ടുകൾ സാധാരണയായി സുരക്ഷിതമാണ്. കടം തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കാത്ത സാഹചര്യത്തിൽ, നിക്ഷേപകന് പണം നൽകാൻ വായ്പ നൽകുന്നയാൾ പ്രത്യേക ആസ്തികൾ വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നു. എന്നാൽ ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ സുരക്ഷിതമല്ല. അതായത്, വായ്പ നൽകുന്ന കമ്പനി ഡെബഞ്ചർ തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കുന്നില്ലെങ്കിൽ, നിക്ഷേപകന് പണം നഷ്ടപ്പെടും.
അപകടസാധ്യതയും വരുമാനവും: സുരക്ഷയില്ലാത്തതിനാൽ, സമാന ക്രെഡിറ്റ് റേറ്റിംഗുള്ള ബോണ്ടുകളെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച് ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ സാധാരണയായി കൂടുതൽ പലിശ നിരക്ക് നൽകുന്നു. ഇത് നിക്ഷേപകർ ഏറ്റെടുക്കുന്ന അധിക അപകടസാധ്യതയ്ക്ക് നഷ്ടപരിഹാരം നൽകുന്നു.
ഡെബഞ്ചറുകളുടെ തരങ്ങൾ:
തിരിച്ചുപിടിക്കാവുന്ന ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ: ഈ ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾക്ക് ഒരു മെച്യൂരിറ്റി തീയതി ഉണ്ട്, ആ തീയതിയിൽ വായ്പ നൽകുന്നയാൾ മുഖവില തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കാൻ ബാധ്യസ്ഥനാണ്.
തിരിച്ചുപിടിക്കാൻ കഴിയാത്ത ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ: ഈ ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾക്ക് ഒരു നിശ്ചിത മെച്യൂരിറ്റി തീയതി ഇല്ല. വായ്പ നൽകുന്നയാൾക്ക് ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിന് ശേഷം അവ തിരിച്ചുപിടിക്കാം, എന്നാൽ അങ്ങനെ ചെയ്യാൻ അവർ ബാധ്യസ്ഥരല്ല.
മാറ്റാവുന്ന ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ: ഈ ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത വിലയ്ക്കും അനുപാതത്തിലും വായ്പ നൽകുന്ന കമ്പനിയുടെ ഓഹരികളായി മാറ്റാം.
ഡെബഞ്ചറിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നത്:
കൂടുതൽ അപകടസാധ്യത: സുരക്ഷിതമായ ബോണ്ടുകളെ അപേക്ഷിച്ച് ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾക്ക് ഡിഫോൾട്ട് സാധ്യത കൂടുതലാണ്. നിക്ഷേപകർ ഡെബഞ്ചറിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിനുമുമ്പ് വായ്പ നൽകുന്ന കമ്പനിയുടെ ക്രെഡിറ്റ് യോഗ്യത ശ്രദ്ധാപൂർവ്വം വിലയിരുത്തേണ്ടതുണ്ട്.
ആർക്ക് അനുയോജ്യം: ബോണ്ടുകളേക്കാൾ കൂടുതൽ വരുമാനം നേടാൻ ആഗ്രഹിക്കുകയും അധിക അപകടസാധ്യത ഏറ്റെടുക്കാൻ തയ്യാറാകുകയും ചെയ്യുന്ന നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഡെബഞ്ചറുകൾ അനുയോജ്യമാകും.
BONDS IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET
n the Indian stock market, bonds are essentially debt instruments issued by companies or the government to raise capital. When you buy a bond, you are essentially loaning money to the issuer for a predetermined period at a fixed interest rate.
Here's a breakdown of bonds in the Indian context:
Types of Bonds:
Government Bonds: These are issued by the Indian government and are considered to be the safest investment option among bonds. They offer lower interest rates compared to corporate bonds but carry minimal risk of default. Examples include Treasury Bills, Government of India (GOI) Bonds.
Corporate Bonds: These are issued by companies to raise funds for various purposes like expansion projects or debt refinancing. They typically offer higher interest rates than government bonds but carry a higher risk of default if the company encounters financial difficulties.
How Bonds Work:
Issuance: A company or the government needs to raise capital and issues bonds with a specific face value (principal amount), interest rate (coupon rate), and maturity date.
Investment: Investors purchase the bonds at the issuance price, which can be at par (face value), above par, or below par depending on market conditions.
Interest Payments: Throughout the bond's tenure, the issuer makes periodic interest payments (coupons) to the bondholders at the predetermined rate.
Maturity: Upon reaching the maturity date, the issuer repays the bond's face value to the investor.
Benefits of Investing in Bonds:
Regular Income: Bonds provide a steady stream of income through regular coupon payments.
Diversification: Bonds can help diversify your investment portfolio and reduce overall risk. They tend to have a negative correlation with stocks, meaning when stock prices fall, bond prices may rise (and vice versa).
Lower Risk: Compared to stocks, bonds generally carry lower risk of price fluctuations, especially government bonds.
Things to Consider When Investing in Bonds:
Credit Rating: The credit rating of the bond issuer reflects their ability to repay the debt. Higher credit ratings indicate lower default risk but also lower interest rates.
Interest Rate Risk: Bond prices are inversely proportional to interest rates. When interest rates rise, existing bonds tend to fall in value.
Liquidity: While some bonds are highly liquid and can be easily traded on the secondary market, others may have limitations on tradability.
Overall, bonds can be a valuable addition to your investment portfolio, especially for those seeking regular income and capital preservation. However, it's crucial to understand the risks involved and choose bonds that align with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
ബോണ്ടുകൾ എന്താണ്?
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ, ബോണ്ടുകൾ കമ്പനികളോ സർക്കാരോ പണം സമാഹരിക്കാൻ പുറത്തിറക്കുന്ന കടപ്പത്രങ്ങളാണ്. നിങ്ങൾ ഒരു ബോണ്ട് വാങ്ങുമ്പോൾ, നിങ്ങൾ വാസ്തവത്തിൽ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത കാലയളവിന് ഒരു നിശ്ചിത പലിശ നിരക്കിൽ വായ്പ നൽകുകയാണ്.
ബോണ്ടുകളുടെ തരങ്ങൾ:
സർക്കാർ ബോണ്ടുകൾ: ഇവ ഇന്ത്യൻ സർക്കാർ പുറത്തിറക്കുന്നതാണ്, ഏറ്റവും സുരക്ഷിതമായ നിക്ഷേപങ്ങളായി കണക്കാക്കപ്പെടുന്നു. സർക്കാർ ബോണ്ടുകൾ കോർപ്പറേറ്റ് ബോണ്ടുകളേക്കാൾ കുറഞ്ഞ പലിശ നിരക്ക് നൽകുന്നു, എന്നാൽ വായ്പ നഷ്ടപ്പെടാനുള്ള സാധ്യത കുറവാണ്. ട്രഷറി ബില്ലുകൾ, ഗവൺമെന്റ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (GOI) ബോണ്ടുകൾ എന്നിവയാണ് ഉദാഹരണങ്ങൾ.
കോർപ്പറേറ്റ് ബോണ്ടുകൾ: ഇവ കമ്പനികൾ പുറത്തിറക്കുന്നതാണ്, വിപുലീകരണ പദ്ധതികൾക്കോ കടം തിരിച്ചടയ്ക്കലിനോ പോലുള്ള വിവിധ ആവശ്യങ്ങൾക്കായി പണം സമാഹരിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു. സർക്കാർ ബോണ്ടുകളേക്കാൾ കോർപ്പറേറ്റ് ബോണ്ടുകൾ ഉയർന്ന പലിശ നിരക്ക് നൽകുന്നു, എന്നാൽ വായ്പ നഷ്ടപ്പെടാനുള്ള സാധ്യത കൂടുതലാണ്.
ബോണ്ടുകൾ എങ്ങനെ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു:
പുറത്തിറക്കൽ: ഒരു കമ്പനി അല്ലെങ്കിൽ സർക്കാർ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത മുഖവില (principal amount), പലിശ നിരക്ക് (coupon rate), മെച്യൂരിറ്റി തീയതി എന്നിവയോടെ ബോണ്ടുകൾ പുറത്തിറക്കുന്നു.
നിക്ഷേപം: നിക്ഷേപകർ പുറത്തിറക്കൽ വിലയിൽ ബോണ്ടുകൾ വാങ്ങുന്നു, ഇത് മുഖവിലയ്ക്ക് തുല്യമാകാം, അതിനേക്കാൾ കൂടുതലോ കുറവോ ആകാം, വിപണി സാഹചര്യങ്ങളെ ആശ്രയിച്ച്.
പലിശ പണമടയ്ക്കൽ: ബോണ്ടിന്റെ കാലയളവിൽ, പുറത്തിറക്കുന്നയാൾ നിശ്ചിത ഇടവേളകളിൽ (സാധാരണയായി പ്രതിമാസം അല്ലെങ്കിൽ വാർഷികം) ബോണ്ട് ഉടമകൾക്ക് പലിശ പണമടയ്ക്കുന്നു.
മെച്യൂരിറ്റി: മെച്യൂരിറ്റി തീയതി എത്തിക്കഴിഞ്ഞാൽ, പുറത്തിറക്കുന്നയാൾ ബോണ്ടിന്റെ മുഖവില നിക്ഷേപകന് തിരികെ നൽകുന്നു.
ബോണ്ടുകളിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിന്റെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
സ്ഥിരമായ വരുമാനം: ബോണ്ടുകൾ പതിവായി പലിശ പണമടയ്ക്കുന്നു, ഇത് സ്ഥിരമായ വരുമാന സ്രോതസ്സ് നൽകുന്നു.
വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം: ബോണ്ടുകൾ നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപ പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരിക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കും, ഇത് മൊത്തത്തിലുള്ള അപകടസാധ്യത കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു.
📷
Mutual Funds in the Indian Stock Market
A mutual fund in the Indian stock market is a pooled investment vehicle that allows you to invest alongside other individuals in a professionally managed basket of assets. Here's how it works:
Structure:
Asset Management Company (AMC): Creates and manages the mutual fund scheme, outlining its investment objectives and risk profile.
Investors: Contribute money to the fund by purchasing units at the Net Asset Value (NAV). NAV represents the market value of the fund's underlying assets divided by the number of outstanding units.
Fund Manager: A professional employed by the AMC who actively manages the fund's portfolio by buying and selling stocks, bonds, or other securities according to the fund's objectives.
Working of a Mutual Fund:
Investment: You invest in a mutual fund by purchasing units at the current NAV.
Portfolio Management: The fund manager utilizes your money, along with funds from other investors, to build a diversified portfolio aligned with the fund's goals (growth, income, etc.).
Earnings and NAV Fluctuation: As the underlying assets' value fluctuates in the market, the fund's NAV also changes. If the holdings increase in value, the NAV goes up, and vice versa.
Returns: Profits from dividends or selling securities at a higher price are reflected in the NAV increase. You earn returns based on the NAV movement when you redeem your units (sell them back to the fund).
Benefits of Mutual Funds:
Diversification: Reduces risk by spreading your investment across various assets.
Professional Management: Experts manage the fund, saving you time and research efforts.
Affordability: Invest with smaller amounts compared to buying individual stocks.
Liquidity: Easily redeem your units for cash (depending on the fund type).
Types of Mutual Funds in India:
Equity Funds: Invest primarily in stocks for capital appreciation.
Debt Funds: Invest in fixed-income securities like bonds for regular income.
Hybrid Funds: A mix of equity and debt, offering a balance of growth and income.
Things to Consider Before Investing:
Investment Objective: Align the fund's objective with your financial goals (retirement, short-term gains, etc.).
Risk Tolerance: Understand the inherent risk associated with different fund types.
Investment Horizon: How long you plan to stay invested in the fund.
Expense Ratio: The annual fee charged by the AMC for managing the fund.
Regulation:
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) regulates mutual funds in India, ensuring investor protection and fair market practices.
മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകൾ
ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിൽ, നിക്ഷേപകർക്ക് ഒരുമിച്ച് പണം നിക്ഷേപിക്കാനും ഒരു പ്രൊഫഷണൽ ടീം നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്ന വിവിധ ആസ്തികളുടെ ഒരു കൂട്ടത്തിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കാനും അവസരം നൽകുന്ന ഒരു സംഘടിത നിക്ഷേപ സംവിധാനമാണ് മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകൾ.
ഘടന:
ആസ്തി മാനേജ്മെന്റ് കമ്പനി (AMC): മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ട് സ്കീം സൃഷ്ടിക്കുകയും കൈകാര്യം ചെയ്യുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഓരോ സ്കീമിനും നിക്ഷേപ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങളും അപകടസാധ്യതയും ഉണ്ടാകും.
നിക്ഷേപകർ: നിലവിലെ NAV-ൽ യൂണിറ്റുകൾ വാങ്ങിക്കൊണ്ട് ഫണ്ടിൽ പണം നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നു. NAV എന്നത് ഫണ്ടിന്റെ അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തികളുടെ വിപണി മൂല്യം യൂണിറ്റുകളുടെ എണ്ണത്താൽ ഹരിച്ചാൽ ലഭിക്കുന്നതാണ്.
ഫണ്ട് മാനേജർ: AMC യൊന്നാൽ നിയമിക്കപ്പെട്ട ഒരു പ്രൊഫഷണൽ, ഫണ്ടിന്റെ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾക്കനുസൃതമായി ഓഹരികൾ, ബോണ്ടുകൾ, മറ്റ് സെക്യൂരിറ്റികൾ എന്നിവ വാങ്ങിയും വിൽക്കയും ചെയ്തുകൊണ്ട് ഫണ്ടിന്റെ പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ സജീവമായി നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നു.
മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ട് എങ്ങനെ പ്രവർത്തിക്കുന്നു:
നിക്ഷേപം: നിങ്ങൾ നിലവിലെ NAV-ൽ യൂണിറ്റുകൾ വാങ്ങിക്കൊണ്ട് ഒരു മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നു.
പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ മാനേജ്മെന്റ്: ഫണ്ട് മാനേജർ നിങ്ങളുടെ പണം മറ്റ് നിക്ഷേപകരുടെ പണവുമായി സംയോജിപ്പിച്ച് ഫണ്ടിന്റെ ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾക്കനുസൃതമായി (വളർച്ച, വരുമാനം, തുടങ്ങിയവ) ഒരു വൈവിധ്യമാർന്ന പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ നിർമ്മിക്കാൻ ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
വരുമാനവും NAV ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിലും: അടിസ്ഥാന ആസ്തികളുടെ വിപണി മൂല്യം ഏറ്റക്കുറച്ചിൽ വരുത്തുമ്പോൾ ഫണ്ടിന്റെ NAV-യും മാറുന്നു. ഹോൾഡിംഗ്സിന്റെ മൂല്യം വർദ്ധിക്കുകയാണെങ്കിൽ NAV ഉയരുകയും വില കുറയുകയാണെങ്കിൽ NAV താഴുകയും ചെയ്യും.
മടക്കം: നിങ്ങൾ യൂണിറ്റുകൾ തിരിച്ചു വിൽക്കുമ്പോൾ (ഫണ്ടിന് തിരികെ വിൽക്കുമ്പോൾ) NAV-ലെ മാറ്റത്തെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ലാഭം ലഭിക്കും.
മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകളുടെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
വൈവിധ്യവൽക്കരണം: നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപം വിവിധ ആസ്തികളിലേക്ക് വ്യാപിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ അപകടസാധ്യത കുറയ്ക്കുന്നു.
പ്രൊഫഷണൽ മാനേജ്മെന്റ്: സമയവും ഗവേഷണ പരിശ്രമവും ലാഭിക്കാൻ വിദഗ്ധർ ഫണ്ട് നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നു.
WHAT ARE THE RISK IN MUTUAL FUND INVESTMENT
While mutual funds offer diversification and professional management, they are not without risks. Here are some of the key risks to consider when investing in mutual funds:
Market Risk: This is the inherent volatility associated with the stock market. The value of the underlying
assets in a mutual fund (stocks, bonds, etc.) can fluctuate, causing the fund's Net Asset Value (NAV) to go up or down. This means your investment may While mutual funds offer diversification and professional management, they are not without risks. Here are some of the key risks to consider when investing in mutual funds:
Market Risk: This is the inherent volatility associated with the stock market. The value of the underlbe worth less than what you invested initially.
Credit Risk: This risk applies specifically to debt funds that invest in bonds. If the bond issuer defaults on their debt, the fund may not be able to repay your investment in full. The risk is higher for lower-rated bonds that offer higher potential returns.
Interest Rate Risk: This risk is relevant for debt funds. When interest rates rise, the value of existing bonds tends to fall. This can negatively impact the NAV of debt funds, especially those holding longer-term bonds.
Inflation Risk: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your money over time. If the return on your mutual fund investment doesn't keep pace with inflation, you may lose real value on your investment.
Liquidity Risk: While some mutual funds are highly liquid (easy to redeem your units for cash), others may have lock-in periods or exit loads. This can limit your ability to access your money when you need it.
Managerial Risk: The performance of a mutual fund heavily relies on the skill and experience of the fund manager. Even with diversification, a poor investment strategy by the manager can lead to losses for the fund.
Expense Ratio: Mutual funds charge fees to cover management and operational costs. These fees, called the Expense Ratio, can eat into your returns. Higher expense ratios can lower your overall profit.
Other Risks: Depending on the specific type of mutual fund, there could be additional risks like currency risk (for international funds) or concentration risk (if the fund is heavily invested in a few companies or sectors).
Mitigating Risks:
Diversification: Invest in a mix of mutual funds across different asset classes (equity, debt) and market capitalizations (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap) to spread your risk.
Investment Horizon: Invest with a long-term perspective to ride out market fluctuations.
Choose the Right Fund: Select a fund that aligns with your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Review Regularly: Monitor your portfolio performance and make adjustments as needed.
By understanding these risks and taking steps to mitigate them, you can make informed investment decisions with mutual funds.
📷
SIP IN INDIAN STOCK MARKET
Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) in the Indian Stock Market
A Systematic Investment Plan (SIP) is a popular investment strategy used in the Indian stock market that allows you to invest a fixed amount of money at regular intervals (usually monthly) into a chosen mutual fund scheme or directly into stocks. It's like a recurring deposit for the stock market.
Benefits of SIP:
Rupee-Cost Averaging: SIP helps average out the cost per unit of your investment. By investing a fixed amount periodically, you buy more units when the price is low and fewer units when the price is high. This helps to reduce the overall impact of market volatility on your investment.
Discipline: SIP enforces a disciplined approach to investing. You set up a plan and automatically invest a certain amount regularly, regardless of market conditions. This helps you avoid emotional investment decisions based on market highs and lows.
Start Small, Grow Big: SIP allows you to start investing with a small amount, making it accessible to almost anyone. You can gradually increase your SIP amount as your income grows.
Long-Term Wealth Creation: SIP is a long-term investment strategy suitable for building wealth over time. By consistently investing, you benefit from the power of compounding, where your returns are reinvested and earn further returns.
How SIP Works:
Choose Your Investment: Decide if you want to invest in a mutual fund SIP or a stock SIP. Research different options based on your risk tolerance and investment goals.
Set Up SIP: Once you've chosen your investment, approach your broker or mutual fund company and set up an SIP. Specify the investment amount, frequency (monthly, quarterly, etc.), and duration.
Automatic Investment: The chosen amount will be automatically deducted from your bank account at the designated intervals and invested in your chosen mutual fund scheme or stock.
Types of SIP:
Mutual Fund SIP: Invest in a diversified basket of assets managed by professionals.
Stock SIP: Invest directly in individual stocks of your choice. (Requires more research and carries higher risk)
Important Considerations:
Investment Horizon: SIP is a long-term strategy. Ideally, you should invest for at least 5-10 years to benefit from compounding.
Risk Tolerance: SIP does not eliminate risk, but it helps manage it through rupee-cost averaging. Choose an investment that aligns with your risk tolerance.
Review Regularly: Periodically monitor your SIP performance and adjust your investment amount or strategy as needed.
SIP is a powerful tool for disciplined and long-term investing in the Indian stock market. It can help you achieve your financial goals by accumulating wealth gradually and minimizing the impact of market fluctuations.
SIP എന്താണെന്നു വിശദമാക്കുക
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ SIP എന്നാൽ സിസ്റ്റമാറ്റിക് ഇൻവെസ്റ്റ്മെന്റ് പ്ലാൻ (Systematic Investment Plan) എന്നാണ്. ഇത് ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ നിക്ഷേപിക്കാനുള്ള ഒരു ജനപ്രിയ രീതിയാണ്. ഇതിലൂടെ നിങ്ങൾ തിരഞ്ഞെടുത്ത മ്യൂച്ച്വൽ ഫണ്ട് സ്കീമിലോ നേരിട്ട് ഓഹരികളിലോ ഒരു നിശ്ചിത തുകയ്ക്ക് പതിവായി (സാധാരണയായി പ്രതിമാസം) നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നു. ഇത് ഓഹരി വിപണിക്ക് വേണ്ടിയുള്ള ആവർത്തന നിക്ഷേപം പോലെയാണ്.
SIP യുടെ ഗുണങ്ങൾ:
രൂപാ-കോസ്റ്റ് എവറേജിംഗ് (Rupee-Cost Averaging): നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപത്തിന്റെ യൂണിറ്റിന് വില ശരാശരിയാക്കാൻ SIP സഹായിക്കുന്നു. ഒരു നിശ്ചിത തുക പതിവായി നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ, വില കുറഞ്ഞിരിക്കുമ്പോൾ കൂടുതൽ യൂണിറ്റുകളും വില കൂടുതലുള്ളപ്പോൾ കുറച്ച് യൂണിറ്റുകളും നിങ്ങൾക്ക് വാങ്ങാം. ഇത് വിപണി വില സ്വാധീനം നിങ്ങളുടെ നിക്ഷേപത്തിൽ കുറയ്ക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
നിയന്ത്രണം (Discipline): നിക്ഷേപത്തിന്റെ കാര്യത്തിൽ SIP നിങ്ങളെ ധൃതരാടിത്തം പാലിക്കാൻ പ്രേരിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. നിങ്ങൾ ഒരു പ്ലാൻ സജ്ജീകരിക്കുകയും വിപണി സാഹചര്യങ്ങൾ എന്തുതന്നെയായാലും ഒരു നിശ്ചിത തുക പതിവായി നിക്ഷേപിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു. ഇത് വിപണി ഉയർച്ച താഴ്ചകളെ അടിസ്ഥാനമാക്കി വികാരാധീനതയിൽ നിക്ഷേപ തീരുമാനങ്ങൾ എടുക്കുന്നത് ഒഴിവാക്കാൻ സഹായിക്കുന്നു.
ചെറുതായി തുടങ്ങി വലുതായി വളരുക (Start Small, Grow Big): SIP നിങ്ങളെ കുറഞ്ഞ തുകയിൽ നിക്ഷേപം ആരംഭിക്കാൻ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു, ഇത് σχεδόν എല്ലാവർക്കും പ്രാപ് accessible ആക്കുന്നു. നിങ്ങളുടെ വരുമാനം വർദ്ധിക്കുന്തോറും നിങ്ങളുടെ SIP തുക ക്രമേണ വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യാം.
ദീർഘകാല സ്വത്ത് സൃഷ്ട്ടിക്കൽ (Long-Term Wealth Creation): SIP ദീർഘകാലാടിസ്ഥാനത്തിൽ സ്വത്ത് വളർത്താനുള്ള ഒരു നിക്ഷേപ തന്ത്രമാണ്. സ്ഥിരമായി നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിലൂടെ, നിങ്ങളുടെ ആദായം പുനർനിക്ഷേപിക്കപ്പെടുകയും കൂടുതൽ ആദായം നേടുകയും ചെയ്യുന്ന സംയുക്ത പലിശയുടെ (compounding) പ്രയോജനം നിങ്ങൾക്ക് ലഭിക്കുന്നു.
📷
how to identify an asset management company (AMC, MUTUAL FUND) is SEBI approved or not?
📷
how to identify an asset management company (AMC, MUTUAL FUND) is SEBI approved or not?
Here's how you can check if an asset management company (AMC) is SEBI-approved in India:
1. SEBI website:
Visit the SEBI website: [SEBI official website ON sebi.gov.in]
Go to the "Intermediaries" section.
You'll find options for "List of Registered Investment Managers" or "List of SEBI Registered Intermediaries."
These lists will allow you to search by keyword (AMC name) or filter by category (Asset Management Company).
If the AMC is SEBI-approved, it will be listed with its registration details.
2. AMC website:
Most SEBI-approved AMCs will prominently display their SEBI registration number on their official website.
Look for a section like "About Us," "Disclosures," or "Legal" on the AMC's website.
The SEBI registration number should be clearly mentioned there.
3. SEBI Integrated Search:
SEBI offers an "Integrated Search" option on their website: [SEBI integrated search ON sebi.gov.in]
You can enter the AMC name or other relevant details in the search bar.
If the AMC is SEBI-approved, you should see it listed with its registration information.
Important points to remember:
Always verify the AMC's registration status before investing.
Dealing with a SEBI-approved AMC ensures a certain level of regulatory oversight and investor protection.
SEBI's website is the most reliable source for verifying registration status.
Additional Tips:
You can also contact SEBI directly if you have any doubts about an AMC's registration.
Consider the AMC's track record, investment philosophy, and fees before making an investment decision.
ഒരു Asset Management Company Sebi approved ആണോ എന്ന് എങ്ങനെ ആണ് Identify ചെയ്യുക
ഒരു Asset Management Company (AMC) SEBI അംഗീകാരം ഉള്ളതാണോ എന്ന് തിരിച്ചറിയാൻ താഴെപ്പറയുന്ന മാർഗ്ഗങ്ങൾ ഉപയോഗിക്കാം:
1. SEBI വെബ്സൈറ്റ്:
SEBI യുടെ ഔദ്യോഗിക വെബ്സൈറ്റ് സന്ദർശിക്കുക: [SEBI official website ON sebi.gov.in]
"ഇടനിലക്കാർ" എന്ന വിഭാഗത്തിലേക്ക് പോകുക.
"നിക്ഷേപ മാനേജർമാരുടെ രജിസ്റ്റർ ചെയ്ത പട്ടിക" അല്ലെങ്കിൽ "SEBI രജിസ്റ്റർ ചെയ്ത ഇടനിലക്കാരുടെ പട്ടിക" എന്നിവയ്ക്കുള്ള ഓപ്ഷനുകൾ നിങ്ങൾക്ക് കാണാൻ കഴിയും.
ഈ പട്ടികകളിൽ നിങ്ങൾക്ക് കീവേഡ് (AMC പേര്) ഉപയോഗിച്ച് തിരയാനോ അല്ലെങ്കിൽ വിഭാഗം (ആസ്തി മാനേജ്മെന്റ് കമ്പനി) അനുസരിച്ച് ഫിൽട്ടർ ചെയ്യാനോ കഴിയും.
AMC SEBI അംഗീകാരം ഉള്ളതാണെങ്കിൽ, അത് അതിന്റെ രജിസ്ട്രേഷൻ വിശദാംശങ്ങൾക്കൊപ്പം ലിസ്റ്റുചെയ്യും.
2. AMC വെബ്സൈറ്റ്:
SEBI അംഗീകാരം ഉള്ള മിക്ക AMC-കളും അവരുടെ ഔദ്യോഗിക വെബ്സൈറ്റിൽ അവരുടെ SEBI രജിസ്ട്രേഷൻ നമ്പർ വ്യക്തമായി പ്രദർശിപ്പിക്കും.
AMC-യുടെ വെബ്സൈറ്റിലെ "ഞങ്ങളെക്കുറിച്ച്," "വെളിപ്പെടുത്തലുകൾ," അല്ലെങ്കിൽ "നിയമപരമായ" എന്നിങ്ങനെയുള്ള വിഭാഗങ്ങൾക്കായി നോക്കുക.
SEBI രജിസ്ട്രേഷൻ നമ്പർ അവിടെ വ്യക്തമായി പരാമർശിക്കണം.
3. SEBI സംയോജിത തിരയൽ:
SEBI അവരുടെ വെബ്സൈറ്റിൽ ഒരു "സംയോജിത തിരയൽ" ഓപ്ഷൻ നൽകുന്നു: [SEBI integrated search ON sebi.gov.in]
നിങ്ങൾക്ക് തിരയൽ ബാറിൽ AMC പേരോ മറ്റ് പ്രസക്തമായ വിശദാംശങ്ങളോ നൽകാം.
AMC SEBI അംഗീകാരം ഉള്ളതാണെങ്കിൽ, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് അത് അതിന്റെ രജിസ്ട്രേഷൻ വിവരങ്ങൾക്കൊപ്പം ലിസ്റ്റുചെയ്യുന്നത് കാണാൻ കഴിയും.
ഓർത്തിരിക്കേണ്ട പ്രധാന കാര്യങ്ങൾ:
നിക്ഷേപിക്കുന്നതിന് മുമ്പ് എല്ലായ്പ്പോഴും AMC-യുടെ രജിസ്ട്രേഷൻ നില പരിശോധിക്കുക.
SEBI അംഗീകാരം ഉള്ള ഒരു AMC യുമായി ഇടപഴകുന്നത് ഒരു പ്രതീകാത്മക നിയന്ത്രണ മേൽനോട്ടവും നിക്ഷേപക സംരക്ഷണവും ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നു.
രജിസ്ട്രേഷൻ നില പരിശോധിക്കുന്നതിനുള്ള ഏറ്റവും വിശ്വസനീയമായ ഉറവിടം SEBI വെബ്സൈറ്റാണ്.
കൂടുതൽ നുറുങ്ങുകൾ:
നിങ്ങൾക്ക് AMC-യെക്കുറിച്ച് എന്തെങ്കിലും സംശയം ഉണ്ടെങ്കിൽ, നിങ്ങൾക്ക് നേരിട്ട് SEBI-യെ ബന്ധപ്പെടാം.
WHO IS CONTROLLING INDIAN STOCK MARKET
The Indian stock market is regulated and overseen primarily by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). SEBI is the regulatory body established under the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992, tasked with protecting the interests of investors in securities and promoting the development and regulation of the securities market in India. SEBI regulates various aspects of the stock market, including:
Registration and regulation of stock exchanges, brokers, sub-brokers, and other market intermediaries.
Supervision and enforcement of securities laws and regulations.
Oversight of corporate governance practices among listed companies.
Monitoring and regulation of securities offerings, including initial public offerings (IPOs) and rights issues.
Surveillance and investigation of market manipulation, insider trading, and other fraudulent activities.
Implementation of investor education and awareness programs.
While SEBI plays a central role in regulating the Indian stock market, the market itself is influenced by various stakeholders, including:
Government: Government policies, economic reforms, and fiscal measures can have a significant impact on the stock market.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI): As the central bank of India, RBI's monetary policies, interest rate decisions, and currency interventions can influence the stock market.
Market Participants: Institutional investors, retail investors, foreign investors, and corporate entities contribute to the dynamics of the stock market through their buying and selling activities.
Stock Exchanges: National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) are the primary stock exchanges in India. They provide the platform for trading securities and play a crucial role in market operations and infrastructure.
Overall, while SEBI acts as the primary regulator, the Indian stock market is influenced by a combination of regulatory policies, economic factors, investor sentiment, and market participants.
ഇന്ത്യയ്ക്കുള്ളിൽ ഓഹരികൾ, ബോണ്ടുകൾ, ഡെറിവേറ്റീവുകൾ, മറ്റ് സാമ്പത്തിക ഉപകരണങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയുൾപ്പെടെയുള്ള സെക്യൂരിറ്റികൾ വാങ്ങുന്നതിനും വിൽക്കുന്നതിനുമുള്ള സംവിധാനത്തെയാണ് ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റ് സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നത്. വിവിധ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ, റെഗുലേറ്ററി ബോഡികൾ, മാർക്കറ്റ് പങ്കാളികൾ, സാമ്പത്തിക സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളിലെ ട്രേഡിംഗും നിക്ഷേപവും സുഗമമാക്കുന്ന അടിസ്ഥാന സൗകര്യങ്ങൾ എന്നിവ ഇതിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു.
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ പ്രധാന ഘടകങ്ങൾ:
സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ: ഇന്ത്യയിലെ പ്രാഥമിക സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ നാഷണൽ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (എൻഎസ്ഇ), ബോംബെ സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് (ബിഎസ്ഇ) എന്നിവയാണ്. ഈ എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ അവയിൽ ലിസ്റ്റ് ചെയ്തിട്ടുള്ള ട്രേഡിംഗ് സെക്യൂരിറ്റികൾക്ക് പ്ലാറ്റ്ഫോമുകൾ നൽകുന്നു.
റെഗുലേറ്ററി ബോഡികൾ:
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയുടെ മേൽനോട്ടം വഹിക്കുന്ന പ്രാഥമിക നിയന്ത്രണ അതോറിറ്റി സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (സെബി) ആണ്. നിക്ഷേപക സംരക്ഷണം, വിപണി സമഗ്രത, വിപണി പങ്കാളികളുടെ പ്രവർത്തനം എന്നിവയുൾപ്പെടെ സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് മാർക്കറ്റിൻ്റെ വിവിധ വശങ്ങളെ സെബി നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നു.
മാർക്കറ്റ് പങ്കാളികൾ:
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിൽ റീട്ടെയിൽ നിക്ഷേപകർ, സ്ഥാപന നിക്ഷേപകർ (മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകൾ, ഇൻഷുറൻസ് കമ്പനികൾ, പെൻഷൻ ഫണ്ടുകൾ പോലുള്ളവ), ബ്രോക്കർമാർ, മാർക്കറ്റ് മേക്കർമാർ, ലിസ്റ്റ് ചെയ്ത കമ്പനികൾ എന്നിവയുൾപ്പെടെ വിവിധ പങ്കാളികൾ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു.
സാമ്പത്തിക ഉപകരണങ്ങൾ: ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റ് ഇക്വിറ്റി ഷെയറുകൾ, മുൻഗണനാ ഓഹരികൾ, ബോണ്ടുകൾ, കടപ്പത്രങ്ങൾ, ഡെറിവേറ്റീവുകൾ (ഫ്യൂച്ചറുകളും ഓപ്ഷനുകളും പോലുള്ളവ), എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച്-ട്രേഡഡ് ഫണ്ടുകൾ (ഇടിഎഫ്), മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകൾ എന്നിവയുൾപ്പെടെ വ്യാപാരത്തിനും നിക്ഷേപത്തിനുമായി വിപുലമായ സാമ്പത്തിക ഉപകരണങ്ങൾ വാഗ്ദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നു. .
ട്രേഡിംഗ് മെക്കാനിസങ്ങൾ: ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിലെ ട്രേഡിങ്ങ് സാധാരണയായി ഇലക്ട്രോണിക് ട്രേഡിംഗ് പ്ലാറ്റ്ഫോമുകളിലൂടെയാണ് നിശ്ചിത വ്യാപാര സമയങ്ങളിൽ നടക്കുന്നത്. മാർക്കറ്റ് ഓർഡറുകൾ, ലിമിറ്റ് ഓർഡറുകൾ തുടങ്ങിയ വിവിധ ഓർഡർ തരങ്ങൾ ട്രേഡുകൾ നടപ്പിലാക്കുന്നതിനായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
ക്ലിയറിംഗും സെറ്റിൽമെൻ്റും: ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിലെ ക്ലിയറിംഗും സെറ്റിൽമെൻ്റ് പ്രക്രിയകളും സെക്യൂരിറ്റികളും ഫണ്ടുകളും വാങ്ങുന്നവർക്കും വിൽക്കുന്നവർക്കും ഇടയിൽ സമയബന്ധിതവും കാര്യക്ഷമവുമായ കൈമാറ്റം ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നു. സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകളുമായി ബന്ധപ്പെട്ട ക്ലിയറിംഗ് കോർപ്പറേഷനുകൾ ക്ലിയറിംഗ്, സെറ്റിൽമെൻ്റ് പ്രവർത്തനങ്ങൾ കൈകാര്യം ചെയ്യുന്നു.
റെഗുലേറ്ററി അതോറിറ്റി:
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയെ പ്രധാനമായും നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നത് സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (സെബി) ആണ്. 1988-ൽ സ്ഥാപിതമായതും പിന്നീട് 1992-ൽ സെബി ആക്ട് പ്രകാരം നിയമപരമായ അധികാരങ്ങൾ നൽകപ്പെട്ടതും, സെബിക്ക് ഇന്ത്യയിലെ സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് മാർക്കറ്റ് നിയന്ത്രിക്കാനുള്ള ഉത്തരവാദിത്തമുണ്ട്. നിക്ഷേപകരുടെ താൽപ്പര്യങ്ങൾ സംരക്ഷിക്കുക, സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് മാർക്കറ്റിൻ്റെ വികസനം പ്രോത്സാഹിപ്പിക്കുക, സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് മാർക്കറ്റിനെയും ഇടനിലക്കാരെയും നിയന്ത്രിക്കുക എന്നിവയാണ് ഇതിൻ്റെ പ്രധാന ലക്ഷ്യങ്ങൾ.
സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകൾ, ബ്രോക്കർമാർ, മർച്ചൻ്റ് ബാങ്കർമാർ, മ്യൂച്വൽ ഫണ്ടുകൾ, പോർട്ട്ഫോളിയോ മാനേജർമാർ, ക്രെഡിറ്റ് റേറ്റിംഗ് ഏജൻസികൾ എന്നിവയുൾപ്പെടെ വിവിധ സ്ഥാപനങ്ങളെ സെബി നിയന്ത്രിക്കുന്നു. ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിൻ്റെ സുഗമമായ പ്രവർത്തനവും സമഗ്രതയും ഉറപ്പാക്കുന്നതിന് ഇത് നിയന്ത്രണങ്ങൾ രൂപപ്പെടുത്തുകയും പരിശോധനകളും അന്വേഷണങ്ങളും നടത്തുകയും സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് നിയമങ്ങളും നിയന്ത്രണങ്ങളും പാലിക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു.
INTRADAY TRADING
Intraday trading, also known as day trading, refers to the practice of buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day. In the context of the Indian stock market, intraday trading involves purchasing and selling stocks, derivatives (such as futures and options), or other financial instruments within the trading hours of the respective stock exchanges (usually from 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM Indian Standard Time for the National Stock Exchange and the Bombay Stock Exchange).
Key features of intraday trading in the Indian stock market include:
Short-Term Nature: Intraday trading positions are typically opened and closed within the same trading session, with traders aiming to capitalize on short-term price movements.
Leverage: Intraday traders often use leverage provided by brokers to amplify their trading positions, allowing them to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital.
Risk and Volatility: Intraday trading can involve higher levels of risk and volatility compared to longer-term investing, as traders attempt to profit from short-term price fluctuations.
Technical Analysis: Intraday traders commonly rely on technical analysis techniques, such as chart patterns, technical indicators, and volume analysis, to identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
Margin Trading: Intraday trading often involves margin trading, where traders can buy or sell securities with funds borrowed from their brokers, using the securities held in their trading accounts as collateral.
Brokerage and Costs: Intraday trading typically incurs higher brokerage costs compared to traditional investing, as traders may execute multiple trades throughout the day.
Regulatory Requirements: Intraday trading is subject to regulatory requirements and guidelines set by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI), including margin requirements, position limits, and disclosure norms.
Overall, intraday trading in the Indian stock market offers opportunities for active traders to profit from short-term price movements, but it also involves inherent risks and requires a disciplined approach, proper risk management, and a thorough understanding of market dynamics and trading strategies
ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗ് നിർവചിക്കുക
ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗ്, ഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗ് എന്നും അറിയപ്പെടുന്നു, ഒരേ ട്രേഡിംഗ് ദിവസത്തിനുള്ളിൽ financial instruments (STOCKS)വാങ്ങുകയും വിൽക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്ന രീതിയെ സൂചിപ്പിക്കുന്നു. ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിൻ്റെ പശ്ചാത്തലത്തിൽ, അതത് സ്റ്റോക്ക് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ചുകളുടെ ട്രേഡിംഗ് സമയത്തിനുള്ളിൽ (സാധാരണയായി 9:15 AM മുതൽ 3:30 വരെ) ഓഹരികൾ, ഡെറിവേറ്റീവുകൾ (ഫ്യൂച്ചറുകളും ഓപ്ഷനുകളും പോലുള്ളവ) അല്ലെങ്കിൽ മറ്റ് സാമ്പത്തിക ഉപകരണങ്ങൾ വാങ്ങുന്നതും വിൽക്കുന്നതും ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗിൽ ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു. (usually from 9:15 AM to 3:30 PM Indian Standard Time for the National Stock Exchange and the Bombay Stock Exchange).
ഇന്ത്യൻ ഓഹരി വിപണിയിലെ ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗിൻ്റെ പ്രധാന സവിശേഷതകൾ:
ഹ്രസ്വകാല സ്വഭാവം: ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗ് പൊസിഷനുകൾ സാധാരണയായി ഒരേ ട്രേഡിംഗ് സെഷനിൽ തുറക്കുകയും അടയ്ക്കുകയും ചെയ്യുന്നു, വ്യാപാരികൾ ഹ്രസ്വകാല വില ചലനങ്ങൾ മുതലെടുക്കാൻ ലക്ഷ്യമിടുന്നു.
ലിവറേജ്: ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡർമാർ അവരുടെ ട്രേഡിംഗ് സ്ഥാനങ്ങൾ വർദ്ധിപ്പിക്കുന്നതിന് ബ്രോക്കർമാർ നൽകുന്ന ലിവറേജ് ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു, ഇത് ചെറിയ മൂലധനം ഉപയോഗിച്ച് ഒരു വലിയ സ്ഥാനം നിയന്ത്രിക്കാൻ അവരെ അനുവദിക്കുന്നു.
അപകടസാധ്യതയും അസ്ഥിരതയും: ദീർഘകാല നിക്ഷേപവുമായി താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തുമ്പോൾ ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗിൽ ഉയർന്ന തോതിലുള്ള അപകടസാധ്യതയും ചാഞ്ചാട്ടവും ഉൾപ്പെടാം, കാരണം വ്യാപാരികൾ ഹ്രസ്വകാല വില വ്യതിയാനങ്ങളിൽ നിന്ന് ലാഭം നേടാൻ ശ്രമിക്കുന്നു.
സാങ്കേതിക വിശകലനം: ഇൻട്രാഡേ വ്യാപാരികൾ സാധാരണയായി അവരുടെ ട്രേഡുകൾക്കുള്ള സാധ്യതയുള്ള എൻട്രി, എക്സിറ്റ് പോയിൻ്റുകൾ തിരിച്ചറിയാൻ ചാർട്ട് പാറ്റേണുകൾ, സാങ്കേതിക സൂചകങ്ങൾ, വോളിയം വിശകലനം എന്നിവ പോലുള്ള സാങ്കേതിക വിശകലന സാങ്കേതികതകളെ ആശ്രയിക്കുന്നു.
മാർജിൻ ട്രേഡിംഗ്: ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗിൽ പലപ്പോഴും മാർജിൻ ട്രേഡിങ്ങ് ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു, അവിടെ വ്യാപാരികൾക്ക് അവരുടെ ബ്രോക്കർമാരിൽ നിന്ന് കടമെടുത്ത ഫണ്ടുകൾ ഉപയോഗിച്ച് സെക്യൂരിറ്റികൾ വാങ്ങാനോ വിൽക്കാനോ കഴിയും, അവരുടെ ട്രേഡിംഗ് അക്കൗണ്ടുകളിൽ സൂക്ഷിച്ചിരിക്കുന്ന സെക്യൂരിറ്റികൾ ഈടായി ഉപയോഗിക്കുന്നു.
ബ്രോക്കറേജും ചെലവും: പരമ്പരാഗത നിക്ഷേപവുമായി താരതമ്യപ്പെടുത്തുമ്പോൾ ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗിന് സാധാരണയായി ഉയർന്ന ബ്രോക്കറേജ് ചിലവ് വരും, കാരണം വ്യാപാരികൾ ദിവസം മുഴുവൻ ഒന്നിലധികം ട്രേഡുകൾ നടത്താം.
റെഗുലേറ്ററി ആവശ്യകതകൾ: ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗ്, മാർജിൻ ആവശ്യകതകൾ, സ്ഥാന പരിധികൾ, വെളിപ്പെടുത്തൽ മാനദണ്ഡങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയുൾപ്പെടെ സെക്യൂരിറ്റീസ് ആൻഡ് എക്സ്ചേഞ്ച് ബോർഡ് ഓഫ് ഇന്ത്യ (സെബി) നിശ്ചയിച്ചിട്ടുള്ള നിയന്ത്രണ ആവശ്യകതകൾക്കും മാർഗ്ഗനിർദ്ദേശങ്ങൾക്കും വിധേയമാണ്.
മൊത്തത്തിൽ, ഇന്ത്യൻ സ്റ്റോക്ക് മാർക്കറ്റിലെ ഇൻട്രാഡേ ട്രേഡിംഗ് സജീവ വ്യാപാരികൾക്ക് ഹ്രസ്വകാല വില ചലനങ്ങളിൽ നിന്ന് ലാഭം നേടാനുള്ള അവസരങ്ങൾ പ്രദാനം ചെയ്യുന്നു, എന്നാൽ അതിൽ അന്തർലീനമായ അപകടസാധ്യതകളും ഉൾപ്പെടുന്നു,ശരിയായ റിസ്ക് മാനേജ്മെൻ്റ്, മാർക്കറ്റ് ഡൈനാമിക്സ്, ട്രേഡിംഗ് തന്ത്രങ്ങൾ എന്നിവയെക്കുറിച്ച് സമഗ്രമായ ധാരണ ആവശ്യമാണ്.
SINGLE CANDLE STICK ANALYSIS ---------
HAMMER CANDLE STICK PATTERN ---
SHOOTING STAR
SINGLE CANDLE STICK PATTERN
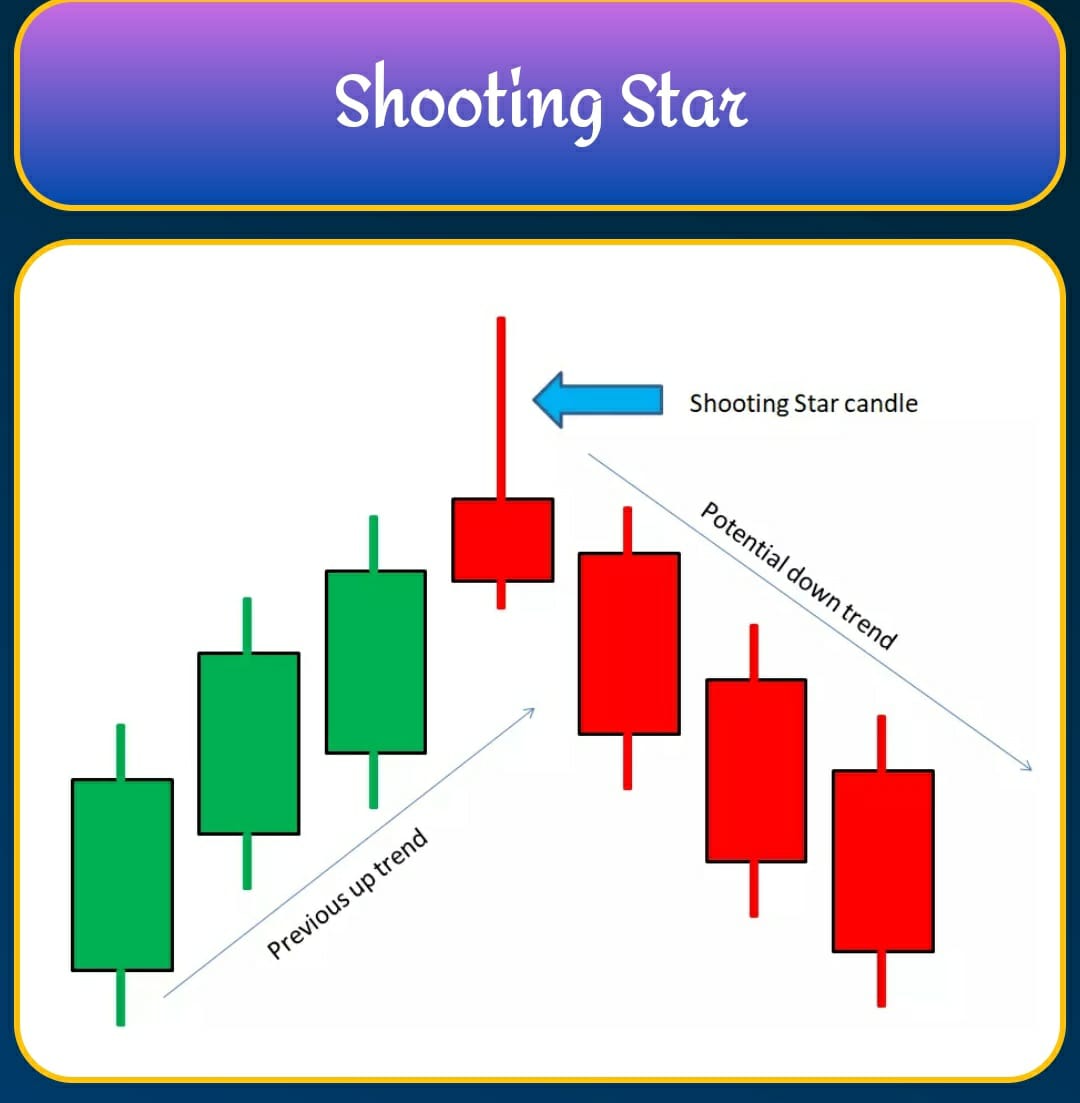
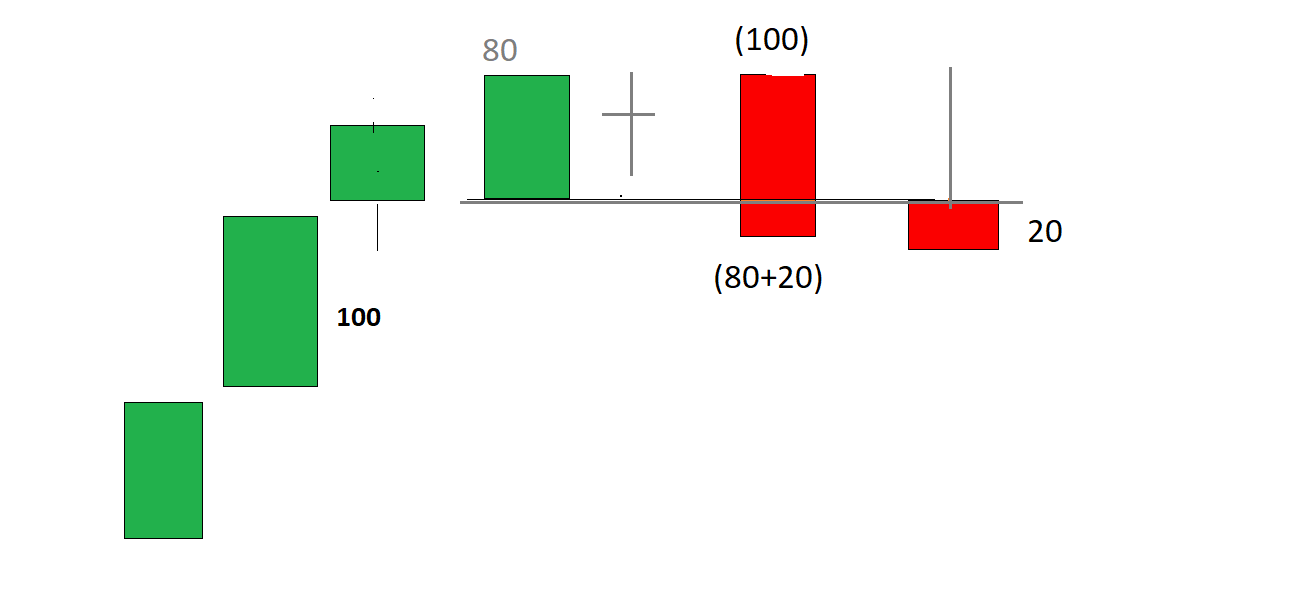
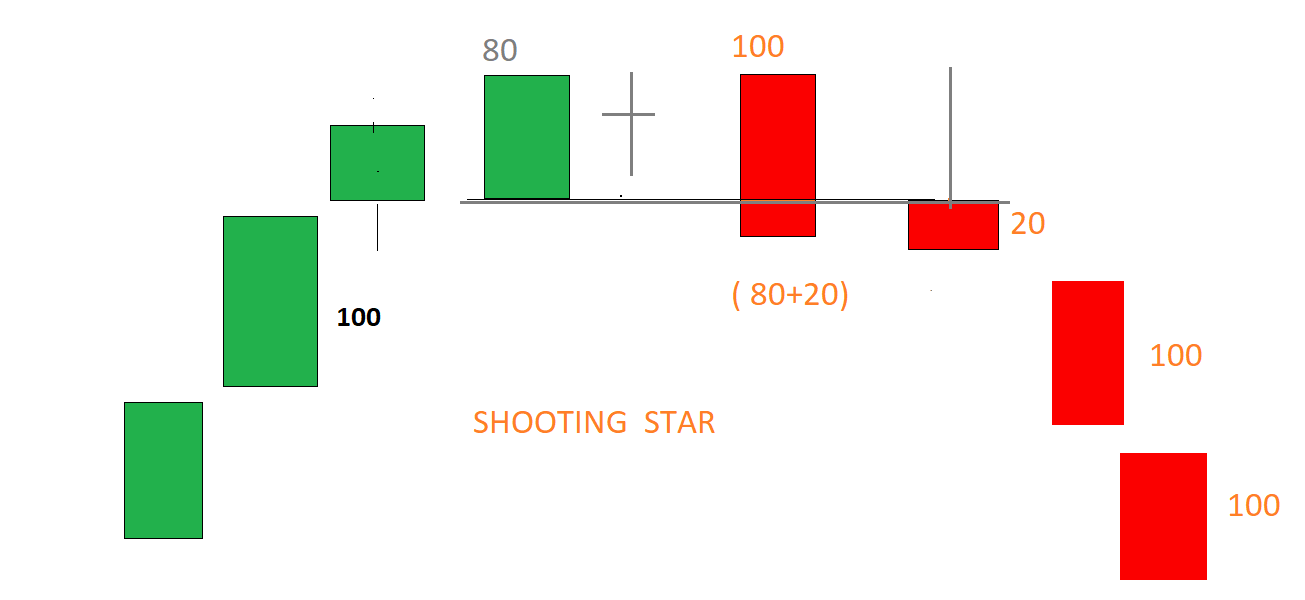
Frequently Asked Questions
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Do you want to know my secret to starting an online business?
Sign up for my newsletter!
Name
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipisicing elit. Autem dolore, alias, numquam enim ab voluptate id quam harum ducimus cupiditate similique quisquam et deserunt, recusandae.
Built with systeme.io
Systeme.io templates pack
Get early access to our new service by registering your interest




Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet